SQL大全_长期更新
前言
Github:https://github.com/HealerJean
1、Mybatis 和 Hibernate
1.1、获取结果为list<map<String,Object>>
1.1.1、mybatis
1、返回类型必须是java.util.HashMap
2、map中的value 必须是Objecrt
1.1.1.1、mapper接口
public interface HealerJeanMapper {
List<Map<String,Object>> sqlMap();
}
1.1.1.2、mapper.xml
<select id="sqlMap" resultType="java.util.HashMap">
SELECT h.id as id ,h.subject as subject FROM healerjean h;
</select>
1.1.1.3、controller测试
@RequestMapping("sqlMap")
@ResponseBody
public List<Map<String,Object>> sqlMap(){
return healerJeanMapper.sqlMap();
}

1.1.2、Jpa分组制作
1.1.2.1、mapper.xml
@Query(value = "select new map(g.department as department,count(*) as count) from GraduateDestination g group by g.department")
List<Map<String,Object>> getAcademyEmplo(String graduateDate);
1.1.2.2、使用
Map<String ,Integer> academyEmploMap=new HashMap<>();
List<Map<String,Object>> list = destinationRepostiory.getAcademyEmplo(graduateDate);
for(Map<String,Object> map:list){
String key = map.get("department").toString() ;
String value = Integer.parseInt(map.get("count").toString()) ;
emploMap.put(key,value);
}
1.2、resultMap作为Mybatis返回类型
1、
property实体类中的属性名2、
column默认是数据表的列名,或者比如
1.2.1、mapper.xml
<select id="select" parameterType="Query" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from scf_contract
</select>
<select id="select" parameterType="Query" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select c.id as user_id from scf_contract c
</select>
1.2.2、resultMap
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.taotao.pojo.TbUser" >
<id column="user_id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT" />
<result column="username" property="username" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="password" property="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="phone" property="phone" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="email" property="email" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="created" property="created" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" />
<result column="updated" property="updated" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" />
</resultMap>
1.3、If标签的使用
<select id="findCustomerList" resultType="com.entity.db.customer.Customer">
SELECT t.* from crm_customer t
WHERE t.isVisiblisVisiblee = 1
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
and t.name like CONCAT('%','${name}','%' )
</if>
<if test="status != null">
and t.status = #{status}
</if>
</select>
1.4、where标签和trim的使用
1、where标签会使sql语句自动加上where
2、 trim标签内sql语句 ,去除 ”前“,”后“ 内容、加前后缀
2.1.suffixOverrides= “,” 去除多余的后缀 ‘,’
2.2.prefixOverrides=”and” 去除多余的前缀 ‘and ‘
**2.3.prefix=”(“ 加前缀 **
**2.4.suffix=”)” 加后缀 **
<select id="selectByExample" parameterType="ScfContractQuery" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<trim suffixOverrides=",">
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
</trim>
from scf_contract
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
</select>
<sql id="Example_Where_Clause">
<where>
<trim prefix="(" prefixOverrides="and" suffix=")">
<if test="refSysFileId != null and refSysFileId != ''">
and ref_sys_file_id = #{refSysFileId,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</if>
</trim>
</where>
</sql>
1.5、foreach标签 的使用
<if test="statusList != null and statusList.size() > 0">
and status in
<foreach collection="list" index="index" item="item"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</if>
1.6、choose when 标签 (相当于if else)的使用
<choose>
<when test="flag == 1">
and t.status = 0
</when>
<when test="flag == 2">
and t.status = 1
</when>
<when test="flag == 3">
and t.expressStatus = 1
</when>
<when test="flag == 4">
and t.status = -2
</when>
<otherwise>
</otherwise>
</choose>
1.7、制作参数map值在mybatis的mapper.xml使用
1.7.1、controller接收参数
@RequestMapping("data")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseBean data(String name,
Integer type,
Integer status,
@RequestParam(value = "page",defaultValue = "0") Integer page){
int pageSize = 15;
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(page,pageSize);
Page<AppInfoData> dataPage = skinsService.findList(pageable,
"name",name,
"type",type,
"status",status);
return ResponseBean.buildSuccess(dataPage);
}
1.7.2、service 制作map参数
pageable 主要是利用里面的参数制作limit参数的
@Override
public Page<AppInfoData> findList(Pageable pageable, Object... param) {
Map data = MyBatisHelper.mergeParameterMap(pageable,param);
if(data.get("startDate") != null){
Date startDate = (Date) data.get("startDate");
data.put("startDate", .DateHelper.getDateFirstTime(startDate));
}
if(data.get("endDate") != null){
Date endDate = (Date) data.get("endDate");
data.put("endDate",DateHelper.getDateLastTime(endDate));
}
List<SkinAppInfoData> dataList = skinsMapper.findSkinList(data);
Long count = skinsMapper.countSkinList(data);
return new PageImpl<SkinAppInfoData>(dataList,pageable,count);
}
1.7.3、MyBatisHelper工具类
public class MyBatisHelper {
public static final String PARAM_OFFSET = "offset";
public static final String PARAM_LIMIT = "limit";
public MyBatisHelper() {
}
public static Map<String, Object> mergeParameterMap(Object... parameter) {
if (parameter.length % 2 != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("parameter须为key-value对应参数");
} else {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < parameter.length; i += 2) {
map.put(parameter[i].toString(), parameter[i + 1]);
}
return map;
}
}
public static Map<String, Object> mergeParameterMap(Pageable pageable, Object... parameter) {
if (parameter.length % 2 != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("parameter须为key-value对应参数");
} else {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("offset", pageable.getOffset());
map.put("limit", pageable.getPageSize());
for(int i = 0; i < parameter.length; i += 2) {
map.put(parameter[i].toString(), parameter[i + 1]);
}
return map;
}
}
}
1.7.4、mapper接口
public interface SkinsMapper {
public List<SkinAppInfoData> findSkinList(Map param);
}
1.7.5、mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.duodian.admore.dao.db.skins.SkinsMapper">
<select id="findSkinList" resultType="com.duodian.admore.data.skins.SkinAppInfoData">
SELECT
A1.`appid`,
A1.`appSecret`,
A1.`icon`,
A1.`makerMemo`,
A1.`haveBackstage`,
A1.`channelJson`,
A1.`filePath`
FROM `skin_app_info_check` a1
where A1.status not in (9)
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND (A1.trackId = #{name}
OR A1.name LIKE CONCAT('%',#{name},'%' )
OR A1.appid LIKE CONCAT('%',#{name},'%' )
OR A1.appSecret LIKE CONCAT('%',#{name},'%' )
)
</if>
<if test="type != null and type != '' ">
and A1.type = #{type}
</if>
<if test="status != null and status != '' ">
and A1.status = #{status}
</if>
order by A1.cdate desc
<if test="offset != null and limit != null">
limit #{offset}, #{limit}
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
1.8、query对象作为参数传入
1.8.1、query对象
public class SysUserQuery implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
private Integer offset;
private Integer limit;
private Date startDate;
private Date endDate ;
private String userid;
private String userParam;
private Integer status;
}
1.8.2、controller层
@RequestMapping("data")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseBean data(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "0")Integer page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "15")Integer pageSize,
SysUserQuery query){
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(page,pageSize);
return ResponseBean.buildSuccess(sysDingUserService.getData(pageable,query));
}
1.8.3、service层,将pageable分页对象放入
@Override
public Page<SysDingUser> getDingUserData(Pageable pageable, SysUserQuery query) {
query.setOffset(pageable.getOffset());
query.setLimit(pageable.getPageSize());
List<SysDingUser> list = sysMapper.findSysDingUserList(query);
Long count = sysMapper.countSysDingUser(query);
return new PageImpl<>(list, pageable, count);
}
}
1.9、resultType 返回对象
1、对于数据库字段匹配的,可以直接选择
2、对于不匹配的使用 as 转化
<select id="findRedStartSpread"
parameterType="com.duodian.RedStartSpreadQuery"
resultType="com.duodian.RedStartHistoryBean">
select
k.trackId,
e.smallIcon,
e.formattedPrice,
e.price,
e.fileSizeBytes,
e.trackName,
f.name admName,
a.nickName userName,
DATE_FORMAT(k.spreadDateStart, '%Y-%m-%d') AS ymd,
k.userId
FROM
redstart_spread k
1.10、不使用注解@Param 只有一个参数传入 `
使用了
@Param正常情况下,直接写参数名字,也可以直接传入数据,但是只有一个参数传入的时候,,不能直接写参数名字了 而是使用下面的_parameter
1.10.1、mapepr接口
List<CustomerChance> getCustomerList(Long adminId);
1.10.2、mapper.xml
<select id="getCustomerList" resultType="com.duodian.db.CustomerChance">
select *
from `crm_customer_chance` c
where c.isVisible = 1
<if test="_parameter != null">
and c.adminId = #{_parameter}
</if>
</select>
1.11、原生符号
被
<![CDATA[]]>这个标记所包含的内容将表示为纯文本,比如<![CDATA[<]]>表示文本内容“<”。
此标记用于xml文档中,我们先来看看使用转义符的情况。我们知道,在xml中,”<”、”>”、”&”等字符是不能直接存入的,否则xml语法检查时会报错,如果想在xml中使用这些符号,必须将其转义为实体
但是经过我测试,在mybaits执行的时候,没有使用 <![CDATA[>]]> 直接 >=也没有提示报错
where rownum <![CDATA[<=]]> #{end,jdbcType=INTEGER} )
1.12、一个条件参数匹配多个 字段
<if test="userParam != null and userParam != ''">
AND (t.userId = #{userParam}
OR a.nickName LIKE CONCAT('%',#{userParam},'%' )
OR b.realName LIKE CONCAT('%',#{userParam},'%' )
OR c.realName LIKE CONCAT('%',#{userParam},'%' )
OR t.customerId LIKE CONCAT('%',#{userParam},'%' )
OR t.customerName LIKE CONCAT('%',#{userParam},'%'))
</if>
1.13、多条件排序
1.13.1、正确的多条件排序,排序字段由前端进行传入${order}
<if test="order != null">
order by ${order}
</if>
1.13.2、chose where进行判断
举例:订单降序 1,订单升序 2 ,成交额降序 3,成交额升序 4,
<select id="findCouponTaoKeDataByParam" resultType="com.duodian.youhui.data.coupon.CouponTaoKeItemGoodSummaryData">
SELECT c.itemTitle,
COUNT(c.itemId) as orderSize,
sum(c.estimateAmount) AS sumEstimateAmount ,
c.adzoneName,c.adzonePid,
c.createTime,c.itemId
FROM coupon_taoke_data c
<where>
c.dataType = 1 and c.status = 1
<include refid="findCouponTaoKeDataByParamSQL"></include>
</where>
GROUP by c.itemId,c.adzonePid
<if test="order != null">
<choose>
<when test="order == 1">
order by orderSize DESC
</when>
<when test="order == 2">
order by orderSize asc
</when>
<when test="order == 3">
order by sumEstimateAmount DESC
</when>
<when test="order == 4">
order by sumEstimateAmount asc
</when>
</choose>
</if>
<if test="offset != null and limit != ''">
limit #{offset}, #{limit}
</if>
</select>
1.13.3、给排序添加非空条件
使用
order by orderid desc实现降序时 ,orderid为null数据的会排在数据的最后面;但是,
order by orderid升序时,orderid为null的数据则会排在最前面 ,如果想要将orderid为null的数据排在最后,就需要加上is null
select * from b_programme u order by u.orderid is null
1.13.4、自定义排序规则
order by field (c.status,'Ready','Part','Completed','Close')
1.14 、参数为0,判断null
id传值为0时(前提是id对应的类型为long 或者 Integer,String型无此问题),发现并没有执行if里的sql,因为在mybatis中会自动把0当成‘’空字符串,
使用时增加多一个or status == 0判断
<if test="status != null and status != '' or status == 0">
1.15、 #和$项目中使用的区别
#{变量名} 可以进行预编译、类型匹配等操作,#{变量名}会转化为jdbc的类型,
#适用于普通的参数传入${变量名} 不进行数据类型匹配,直接替换。
$方式一般用于传入数据库对象,例如传入表名。
1、#方式能够很大程度防止sql注入。因为#会自动转换,而&为直接替换,所以$方式无法防止sql注入
2、项目中的使用,尽量使用# ,少用& 臭小子,明白了吧
select * from tablename where id = #{id}
假设id的值为12
如果id为字符型,那么#{id}表示的就是'12'
如果id为整型, 那么#{id}表示的就是12
select * from tablename where id = ${id}
如果字段id为整型,sql语句就不会出错,但是如果字段id为字符型, 那么sql语句应该写成select * from table where id = '${id}'。
order为 A ASC, A DESC ,B DESC ,B asc数据,这里直接使用#是错误的
<when test="order != null">
order by ${order}
</when>
1.16、返回对象中包含对象 association
1.16.1、mapper
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="ScfUserInfo">
<id column="ID" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="id" />
<result column="username" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="username" />
<result column="real_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="realName" />
<result column="email" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="email" />
<result column="telephone" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="telephone" />
<result column="gender" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="gender" />
<result column="job_number" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="jobNumber" />
<result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" />
<result column="user_type" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userType" />
<result column="ref_company_id" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="refCompanyId" />
<result column="ref_sign_customer_id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="refSignCustomerId" />
<result column="ref_ucenter_id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="refUcenterId" />
<result column="status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="status" />
<result column="create_user" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="createUser" />
<result column="create_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="createName" />
<result column="create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="createTime" />
<result column="update_user" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="updateUser" />
<result column="update_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="updateName" />
<result column="update_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="updateTime" />
<association property="department" javaType="ScfUserDepartment" >
<result column="department_id" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="id" />
<result column="department_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="departmentName" />
<result column="department_desc" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="departmentDesc" />
<result column="pid" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="pid" />
<result column="department_status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="status" />
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserByDepartment" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="ScfUserInfoQuery">
select
u.id,
u.username,
u.real_name,
u.email,
u.telephone,
u.gender,
u.job_number,
u.user_type,
u.ref_company_id,
u.ref_sign_customer_id,
u.status,
d.id as department_id,
d.department_name,
d.department_desc,
d.pid,
d.status as department_status
from scf_user_info u
left join scf_user_ref_user_department rud on rud.ref_user_id = u.id
left join scf_user_department d on rud.ref_department_id = d.id
<where>
<trim prefix="(" prefixOverrides="and" suffix=")">
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and u.username like CONCAT('%', #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR} ,'%')
</if>
</trim>
</where>
</select>
1.16.2、对象实体
@Data
public class ScfUserInfo implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/** 主键 */
private Long id;
/** 用户名 */
private String username;
/** 真实姓名 */
private String realName;
/** 邮箱 */
private String email;
/** 手机号 */
private String telephone;
/** 性别 */
private String gender;
/** 工号 */
private String jobNumber;
/** 密码 */
private String password;
/** 用户类型(字典) */
private String userType;
/** 企业表ID */
private Long refCompanyId;
/** 签章用户ID */
private String refSignCustomerId;
/** 用户状态 */
private String status;
/** 创建人ID */
private Long createUser;
/** 创建人名称 */
private String createName;
/** 创建时间 */
private java.time.LocalDateTime createTime;
/** 更新人 */
private Long updateUser;
/** 更新人名称 */
private String updateName;
/** 更新时间 */
private java.time.LocalDateTime updateTime;
/** 部门 */
private ScfUserDepartment department;
/**
* 用户中心ID
*/
public Long refUcenterId;
}
1.17、 resultType和resultMap的区别
MyBatis中在查询进行select映射的时候,返回类型可以用resultType,也可以用resultMap
resultMap 提供的返回类型是resultMap时,因为Map不能很好表示领域模型,就需要自己再进一步的把它转化为对应的对象,这常常在复杂查询中很有作用。
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.cachee.ilabor.att.clientmodel.User">
<result column="ID" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<result column="SN" property="SN" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="companyId" property="companyId" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="tb_isDelete" property="tb_isDelete" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="tb_createTime" property="tb_createTime" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
</resultMap>
resultType (可以不传入)
resultType 是直接表示返回 Java 类型的 ,其实 MyBatis 的每一个查询映射的返回类型都是ResultMap,MyBatis 会将Map里面的键值对取出赋给 resultType 所指定的对象对应的属性,只是当提供的返回类型属性是 resultType 的时候,MyBatis 对自动的给把对应的值赋给 resultType 所指定对象的属性
1.18、sql 语句中的判断查询
@Query(value = "from JobRequistion j where
j.recruiter=?1
and ( audit.status=?2 or ?2=null)
and (j.title like (%?3%) or ?3=null)
and ( jobCategory=?4 or ?4=null)
and ( jobArea in ?5 or ?5=null)
and j.status=null
and (j.department.name in ?6 or ?6=null)")
public Page<JobRequistion> findList(RecruiterInfo recruiter)
1.19、返回对象中包含枚举
直接映射接口,数据库中存储的将是枚举的
NAME
<resultMap id="resultMap" type="com.healerjean.User">
<result column="insurance_type" property="insuranceType" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
</resultMap>
public class User implements Serializable {
private InsuranceTypeEnum insuranceType;
}
1.20、返回对象中包含集合
1.20.1、List
resultType直接映射即可
1.20.2、Set
下面是逗号分隔的字符串,其实完全可以自己设置(其实和之前在
MybatisPlus加解密类似)
public class User implements Serializable {
private Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> listenMqNodeList;
<resultMap id="resultMap" type="com.healerjean.User">
<result column="listen_mq_node" property="listenMqNodeList" jdbcType="VARCHAR"
typeHandler="com.typehandler.NodeEnumTypeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
@Slf4j
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.VARCHAR)
public class NodeEnumTypeHandler implements TypeHandler<Set<ListenMqNodeEnum>> {
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i,
Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> enums, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (ListenMqNodeEnum listenMqNodeEnum : enums) {
sb.append(listenMqNodeEnum.getCode()).append(",");
}
preparedStatement.setString(i, sb.toString().substring(0, sb.toString().length() - 1));
}
@Override
public Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> getResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
String[] arr = resultSet.getString(s).split(",");
Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> enums = new HashSet<>();
for (String s1 : arr) {
enums.add(ListenMqNodeEnum.getEnumByCode(s1));
}
return enums;
}
@Override
public Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> getResult(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
String[] arr = resultSet.getString(i).split(",");
Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> enums = new HashSet<>();
for (String s1 : arr) {
enums.add(ListenMqNodeEnum.getEnumByCode(s1));
}
return enums;
}
@Override
public Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> getResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i)
throws SQLException {
String[] arr = callableStatement.getString(i).split(",");
Set<ListenMqNodeEnum> enums = new HashSet<>();
for (String s1 : arr) {
enums.add(ListenMqNodeEnum.getEnumByCode(s1));
}
return enums;
}
}
3、表相关
3.1、添加表的备注和字段备注
3.1.1、创建表的时候添加备注
CREATE TABLE `healerjean_comment` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '名字备注',
`email` varchar(64) NOT NULL,
`message` text ,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `index_name` (`name`)
) COMMENT='表名备注' ;
3.1.2、表创建完成添加表名备注和字段备注
ALTER TABLE healerjean_comment COMMENT='测试索引表';
ALTER table healerjean_comment MODIFY name VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '名字备注'
3.2、查询建表语句
show create table table_name ;
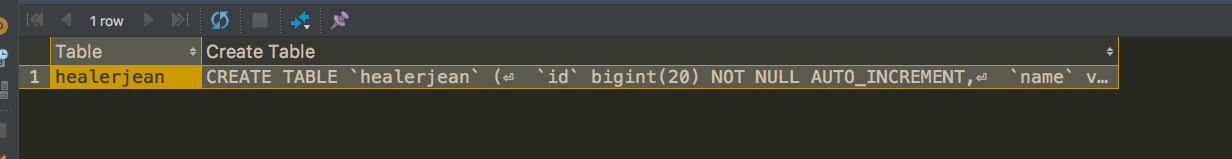
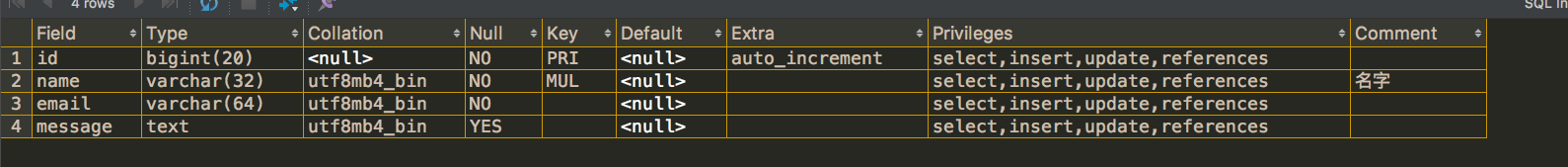
3.3、查看列的属性
show full columns from healerjean;
3.4、修改字段顺序
3.4.1、放到第1位
alter table demo_entity modify name varchar(32) comment '名字' first ;
3.4.2、放到某个字段后面
alter table demo_entity modify name varchar(32) comment '名字' after id ;
3.5、给表添加约束(唯一索引)
这个其实很常见,经常我们会使用主键作为唯一约束,如果是手机用户,或者是邮箱用户进行登录,那么这个登录的字段并不是主键。在高并发,注册的时候,如果不设置唯一约束,则可能会导入两个相同的数据。为了防止这种情况发生,我们要注意添加约束。
创建联合约束,我们发现,这里设置为唯一约束,建立唯一约束和唯一索引又什么区别?建立唯一约束的时候,也会自动的创建唯一索引。建立唯一索引可以说是唯一约束的一种手段。
3.5.1、添加普通和唯一索引
DROP TABLE user_info ;
create table user_info(
id BIGINT(20) not null auto_increment,
fuWuBusinessNoId BIGINT(20) default null,
dingYueBusinessNoId BIGINT(20) default null,
openId varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL UNIQUE ,
iphone varchar(20) default null COMMENT '',
status int(11) default null ,
cdate timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
udate timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
UNIQUE KEY unique_fuWuBusinessNoId_iphone (fuWuBusinessNoId,iphone) COMMENT '服务号和手机号唯一标识一个用户,可用于手机号登录判断',
PRIMARY key (id));
添加普通索引
alter table user_info add index index_name (name);
CREATE INDEX index_name on user_info(name) ;
添加唯一索引
ALTER TABLE user_info add mail VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL ;
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_mail on user_info(mail) ;
alter table user_inf add unique index_mail `user_info` ( mail);
3.5.2、查看索引
show INDEX from user_info ;
3.5.1、删除约束(唯一索引)
ALTER TABLE jw_role DROP INDEX resource_name;
3.5.4、SpringBoot注解
@Table(name = "user_info",
uniqueConstraints = {
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "openId"),
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = {"fuId","iphone"})},
indexes = {
@Index(name = "index_itemGoodId",columnList = "authority,permission",unique = true),
@Index(name = "index_cdate",columnList = "cdate")
})
@Entity
@Accessors(chain = true)
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@ApiModel(description = "微信用户信息")
public class UserInfo {
3.6、给表添加主键
alter table table_name add primary key ("id");
3.7、添加某一列
alter table table_name add ha int;
alter table table_name add ha int before name;
ALTER TABLE `table_name` ADD `service_code` VARCHAR ( 100 ) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL COMMENT '集市服务id' AFTER `insurance_name`,
ADD `sku_id` BIGINT ( 20 ) DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL COMMENT '集市skuId' AFTER `service_code`;
3.8、修改某一列的类型和大小
alter table table_name modify passtest varchar(55);
3.9、删除某一列
alter table table_name drop column passtest;
3.10、修改表的名字
rename table table_name to new_name
3.11、表的字符集
alter table table_name character set utf8;
3.12、修改字段的名字
alter table table_name change column create_data create_time date;
3.13、创建数据库并设置字符集
create database shu character set utf8;
3.14、存储引擎
3.14.1、show engines:查看存储引擎
mysql> SHOW ENGINES ;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.05 sec)
3.14.1、修改表的存储引擎
alter table healerjean_comment ENGINE = MyISAM ;
3.14.2、查看表的存储引擎
show create table table_name ;
3.15、delete,删除表
删除的正确方法
1,delete from user as u where u.userid=6; 错误
2,delete from user u where u.userid=6; 错误
3,delete from user where userid=6; 正确
4,delete u.* from user u where u.userid=6; 正确
5,delete u from user u where u.userid=6; 正确
3.16、truncate清表(不要用delete)
delete删除之后还会占用id,
truncate table_name ;
3.17、select into和 inseret into select 两种表复制语句
http://www.cnblogs.com/freshman0216/archive/2008/08/15/1268316.html
3.17.1、Insert into
要求目标表Table2必须存在,由于目标表Table2已经存在,所以我们除了插入源表Table1的字段外,还可以插入常量。示例如下:
语句形式为:Insert into Table2(field1,field2,…) select value1,value2,… from Table1
Insert into Table2(a, c, d) select a,c,5 from Table1
3.17.2、select * into
要求目标表Table2不存在,因为在插入时会自动创建表Table2,并将Table1中指定字段数据复制到Table2中。
语句形式为:SELECT vale1, value2 into Table2 from Table1
select a,c INTO Table2 from Table1
select ename,sal,job into pname,psal,pjob from emp where empno = eno;
4、数据库相关
4.1、连接数据库
mysql -uroot -ppassword
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot -ppassword
mysql -h 127.0.0.1__ -u root -p
4.2、备份导入数据库
4.2.1、备份数据库
mysqldump -uroot -ppassword database_name > /usr/local/database_name.sql
4.2.2、导入数据库
mysql -uroot -ppassword
create database database_name;
use database_name;
source /usr/local/database_name.sql
复杂查询
1、count
1.1、count(*)、count(id)
如果版本不太高的会报错*(因为没有分组),高级的版本下面这个只会输出一行
SELECT count(*) as "count",idfa from apps_click_record a;
1.2、和group分组一起使用 ,就表示分组之后每组的个数
SELECT count(*) as "count",idfa
from apps_click_record a
WHERE a.keywordId = '169995'
GROUP by idfa
ORDER BY count(*) DESC ;
1.3、count(*) 和 * 的查询 是错误的
下面是错误的
SELECT count(*) as "count",* from apps_click_record a;
1.4、count(distinct Sname)去掉重复得到唯一的数量
select count(distinct b.type) from B b
# 下面这种写法垃圾死了
select count(*) from
(
select b.type from B b group by b.type
) m
2、group by
5.7 版本的 mysql中可能会遇到取唯一值的问题。一定要注意
2.1、分组过滤重复
2.1.1、表中有id和name 两个字段,查询出name重复的所有数据
select *
from healerjean a
where (a.username) in (
select username
from healerjean
group by username
having count(*) > 1
)
2.1.2、删除分组中重读的数据,只保留id最小的记录
1、查询每组重复的用户名
select username from healerjean group by username having count(username) > 1
2、先查询每组重复的id最小的数据
select min(id) from healerjean group by username having count(username)>1
3、判断用户名重复,并排除掉id最小的数据,进行删除
delete from healerjean
where username in (
select username
from healerjean
group by username
having count(username) > 1
)
and id not in (
select min(id)
from healerjean
group by username
having count(username)>1)
2.1.3、查找表中多余的重复记录(多个字段)
select *
from vitae a
where (a.peopleId,a.seq) in (
select peopleId, seq
from vitae
group by peopleId,seq
having count(*) > 1)
2.2、havaing count用法
数据样例
create table tb_grade (
Sno int(11) default 0 comment '学号',
Sname varchar(20) default '' comment '姓名',
Cno int(11) default 0 comment '学号',
Cname varchar(20) default ''comment '课程名',
score int(11) default 0 comment '分数'
) comment '成绩表' ;
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1001, '李菲', 1, '语文', 86);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1001, '李菲', 2, '数学', 50);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1001, '李菲', 3, '英语', 41);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1001, '李菲', 4, '化学', 89);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1001, '李菲', 5, '物理', 20);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1002, '张宇晋', 1, '语文', 86);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1002, '张宇晋', 2, '数学', 50);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1002, '张宇晋', 3, '英语', 70);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1002, '张宇晋', 4, '化学', 89);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1002, '张宇晋', 5, '物理', 20);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1003, '翠花', 1, '语文', 10);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1003, '翠花', 2, '数学', 20);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1003, '翠花', 3, '英语', 70);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1003, '翠花', 4, '化学', 40);
INSERT INTO tb_grade (Sno, Sname, Cno, Cname, score) VALUES (1003, '翠花', 5, '物理', 10);
| Sno | Sname | Cno | Cname | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 李菲 | 1 | 语文 | 86 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 2 | 数学 | 50 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 3 | 英语 | 41 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 4 | 化学 | 89 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 5 | 物理 | 20 |
| 1002 | 张宇晋 | 1 | 语文 | 86 |
| 1002 | 张宇晋 | 2 | 数学 | 50 |
| 1002 | 张宇晋 | 3 | 英语 | 70 |
| 1002 | 张宇晋 | 4 | 化学 | 89 |
| 1002 | 张宇晋 | 5 | 物理 | 20 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 1 | 语文 | 10 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 2 | 数学 | 20 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 3 | 英语 | 70 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 4 | 化学 | 40 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 5 | 物理 | 10 |
1、查询不及格科目数大于等于2的学生学号和学生姓名:
select t.Sno,t.Sname
from tb_grade t
where t.score < 60
group by t.Sno having count(t.Cno) > 2
| Sno | Sname |
|---|---|
| 1001 | 李菲 |
| 1003 | 翠花 |
2、查询不及格科目数大于等于2的学生学号和不及格科目数量:
select t.Sno,
count(t.Cno) as '不及格科目数量'
from tb_grade t
where t.score < 60
group by t.Sno having count(t.Cno) > 2
| Sno | 不及格科目数量 |
|---|---|
| 1001 | 3 |
| 1003 | 4 |
3、查询不及格科目数大于等于2的学生学号、学生姓名、科目号、科目名称和分数,并按学号降序、科目号升序排序
select t.Sno,
t.Sname,
t.Cno,
t.Cname,
t.score
from tb_grade t
where t.score < 60
and t.Sno in (select b.Sno
from tb_grade b
where b.score < 60 group by b.Sno having count(b.Cno) > 2)
order by t.Sno desc, Cno asc;
| Sno | Sname | Cno | Cname | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1003 | 翠花 | 1 | 语文 | 10 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 2 | 数学 | 20 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 4 | 化学 | 40 |
| 1003 | 翠花 | 5 | 物理 | 10 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 2 | 数学 | 50 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 3 | 英语 | 41 |
| 1001 | 李菲 | 5 | 物理 | 20 |
2.3、having中添加and
接上面的举例说明1的数据样例
select t.Sno,t.Sname
from tb_grade t
where t.score < 60
group by t.Sno having count(t.Cno) > 1 and Sname = '李菲';
| Sno | Sname |
|---|---|
| 1001 | 李菲 |
3、join
3.1、内连接 左链接,右连接,全连接
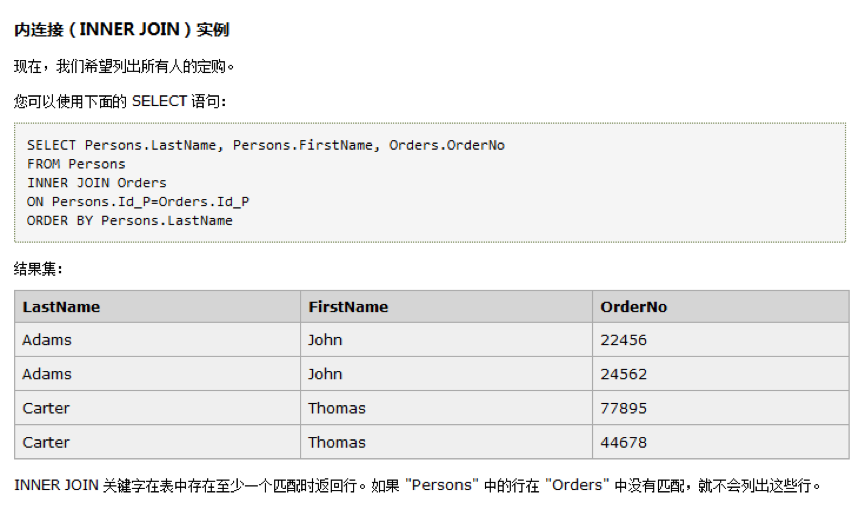
3.1.1、inner join 和 join
解释:返回左表和 右表同时存在的行
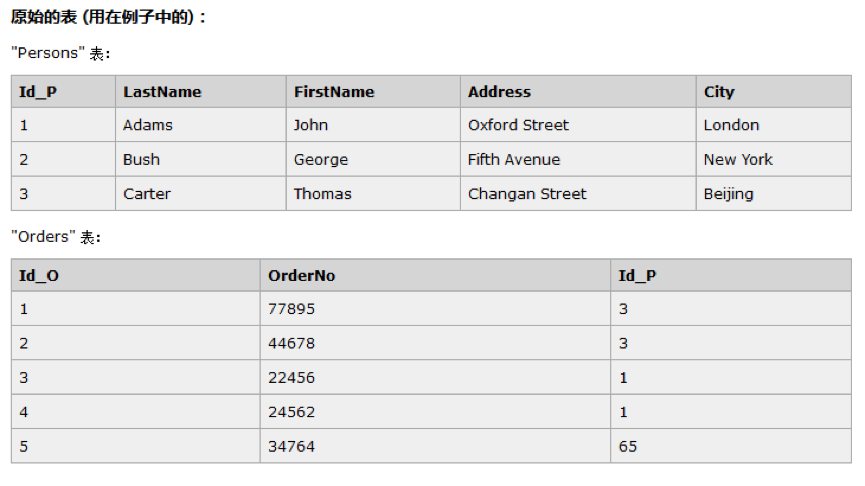
SELECT Persons.LastName, Persons.FirstName, Orders.OrderNo
FROM Persons
INNER JOIN Orders ON Persons.Id_P = Orders.Id_P
ORDER BY Persons.LastName
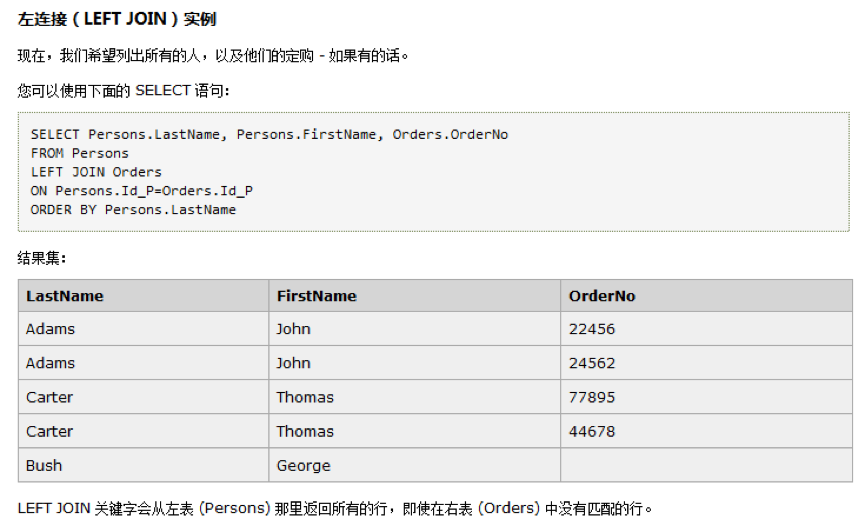
3.1.2、left join
解释:即使右表中没有匹配,也从左表返回所有的行
select Persons.LastName, Persons.FirstName, Orders.OrderNo
from Persons
left join Orders on Persons.Id_P = Orders.Id_P
order by Persons.LastName

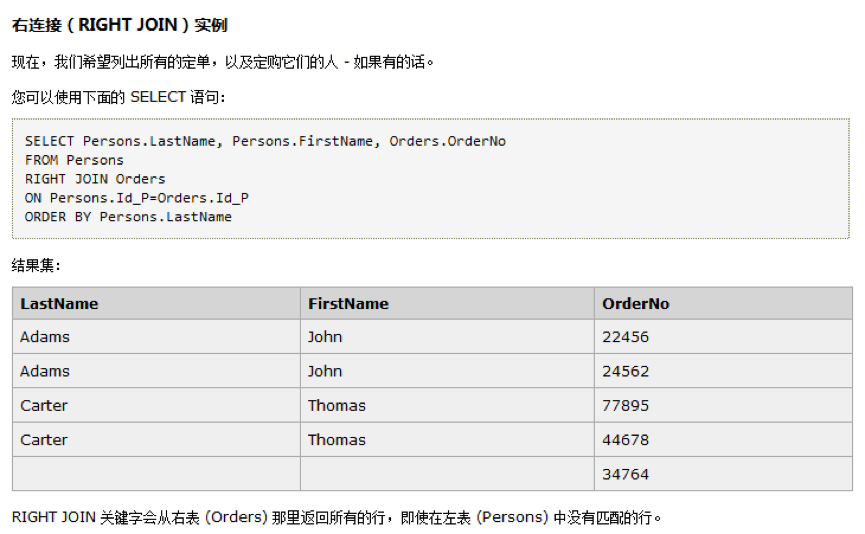
3.1.3、right join
即使左表中没有匹配,也从右表返回所有的行
select Persons.LastName, Persons.FirstName, Orders.OrderNo
from Persons
right join Orders on Persons.Id_P = Orders.Id_P
order by Persons.LastName

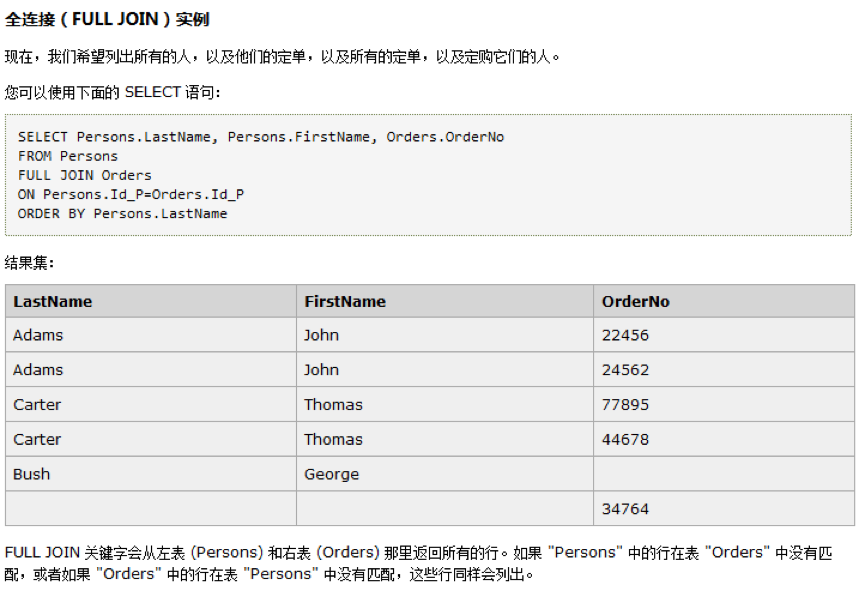
3.1.4、full join
只要其中一个表中存在匹配,就返回行
select Persons.LastName, Persons.FirstName, Orders.OrderNo
from Persons full
join Orders on Persons.Id_P = Orders.Id_P
order by Persons.LastName

3.2、举例说明1
create table department (
dept_id int(11) default 0 comment '部门id',
dept_name varchar(20) default '' comment '部门名称'
)comment ='部门' ;
insert into department values(1,'广告部');
insert into department values(2,'媒体部');
insert into department values(3,'管理部');
select * from department ;
create table employee (
emp_id int(11) default 0 comment '员工id',
emp_name varchar(20) default '' comment '员工名字',
dept_id int(11) default 0 comment '部门id',
emp_wage decimal(19,2) default 0 comment '薪水'
)comment ='员工表' ;
INSERT INTO VALUES (1, '乔峰', 1, 17000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (2, '张三丰', 1, 15000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (3, '段誉', 2, 18000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (4, '虚竹', 2, 12000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (5, '杨过', 3, 16000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (6, '黄老邪', 1, 17000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (7, '黄蓉', 1, 15000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (8, '郭靖', 2, 15000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (9, '金龙法王', 3, 15000.00);
INSERT INTO VALUES (10, '老顽童', 3, 11000.00);
| dept_id | dept_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 |
| 2 | 媒体部 |
| 3 | 管理部 |
| emp_id | emp_name | dept_id | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 乔峰 | 1 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 张三丰 | 1 | 15000.00 |
| 6 | 黄老邪 | 1 | 17000.00 |
| 7 | 黄蓉 | 1 | 15000.00 |
| 3 | 段誉 | 2 | 18000.00 |
| 4 | 虚竹 | 2 | 12000.00 |
| 8 | 郭靖 | 2 | 15000.00 |
| 5 | 杨过 | 3 | 16000.00 |
| 9 | 金龙法王 | 3 | 15000.00 |
| 10 | 老顽童 | 3 | 11000.00 |
3.2.1、left join
select
d.dept_id,
d.dept_name,
e.emp_name,
e.emp_wage
from
department d
left join employee e on e.dept_id = d.dept_id ;
| dept_id | dept_name | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 张宇晋 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 张三丰 | 15000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | 张翠 | 18000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | 林徽因 | 12000.00 |
| 3 | 管理部 | 赵国强 | 17000.00 |
3.2.2、left join on and
先会在副表中对and条件进行过滤,然后再跟左边主表进行关联
1、主表 (只会对副表起作用)
select d.dept_id,
d.dept_name,
e.emp_name,
e.emp_wage
from department d
left join employee e on e.dept_id = d.dept_id and d.dept_id = 1
| dept_id | dept_name | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 张三丰 | 15000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 黄蓉 | 15000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | NULL | NULL |
| 3 | 管理部 | NULL | NULL |
2、副表(只会对副标起作用)
select d.dept_id,
d.dept_name,
e.emp_name,
e.emp_wage
from department d
left join employee e on e.dept_id = d.dept_id and e.emp_wage = 17000
| dept_id | dept_name | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | NULL | NULL |
| 3 | 管理部 | NULL | NULL |
3.2.3、where 实现全部查询结果的过滤
select d.dept_id,
d.dept_name,
e.emp_name,
e.emp_wage
from department d
left join employee e on e.dept_id = d.dept_id
where e.emp_wage = 17000;
| dept_id | dept_name | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
3.2.4、进阶 sql
3.2.43.1、求各个部门的最大工资 和最小工资
1、求各个部门的最大工资 和最小工资
select e.dept_id,
max(emp_wage) as max_exp_wage,
min(emp_wage) as min_exp_wage
from employee e
group by e.dept_id
| dept_id | max_exp_wage | min_exp_wage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17000.00 | 15000.00 |
| 2 | 18000.00 | 12000.00 |
| 3 | 16000.00 | 11000.00 |
上面的查询已经知道部门的最大工资和最小工资了,但是部门的名称还没有查出来,可以关联查出部门的名称(因为是一一对应,所以join查询可以满足)
select d.dept_id,
d.dept_name,
s.max_exp_wage,
s.min_exp_wage
from department d
left join (
select e.dept_id,
max(emp_wage) as max_exp_wage,
min(emp_wage) as min_exp_wage
from employee e
group by e.dept_id
) s on s.dept_id = d.dept_id;
| dept_id | dept_name | max_exp_wage | min_exp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 17000.00 | 15000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | 18000.00 | 12000.00 |
| 3 | 管理部 | 16000.00 | 11000.00 |
3.2.4.2、查询每个部门中最大工资雇员并按照部门排序
需要考虑的是,部门中肯定有工资相同的,那么最大工资也肯定有可能会相同,所以肯定主表是employee
1、先查询每个部门最大的工资
select e.dept_id,
max(e.emp_wage) as max_exp_wage
from employee e
group by e.dept_id
| dept_id | max_exp_wage |
|---|---|
| 1 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 18000.00 |
| 3 | 16000.00 |
2、查询工资是最大工资的雇员
select em.dept_id,
em.emp_id,
em.emp_name,
em.emp_wage
from employee em
join (select e.dept_id, max(emp_wage) as max_exp_wage from employee e group by e.dept_id) s
on s.dept_id = em.dept_id
where em.emp_wage = s.max_exp_wage
order by em.dept_id
| dept_id | emp_id | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 6 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 3 | 段誉 | 18000.00 |
| 3 | 5 | 杨过 | 16000.00 |
3、上面基本上完事了,就差部门没出来,所以关联查询部门即可
select em.dept_id,
de.dept_name,
em.emp_id,
em.emp_name,
em.emp_wage
from employee em
join department de on de.dept_id = em.dept_id
join (select e.dept_id, max(emp_wage) as max_exp_wage from employee e group by e.dept_id) s
on s.dept_id = em.dept_id
where em.emp_wage = s.max_exp_wage
order by em.dept_id
| dept_id | dept_name | emp_id | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 6 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 1 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | 3 | 段誉 | 18000.00 |
| 3 | 管理部 | 5 | 杨过 | 16000.00 |
3.2.4.3、查询大于平均工资的雇员,并按照部门排序
1、先查询各个部门的平均工资
select e.dept_id, avg(e.emp_wage)
from employee e
group by e.dept_id;
| dept_id | AVG(e.emp_wage) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 16000.000000 |
| 2 | 15000.000000 |
| 3 | 14000.000000 |
2、查询工资大于平均工资的雇员,这个时候需要left join(join都可以,因为肯定是一一对应的关系)查询雇员表了
select em.dept_id,
s.avg_wage,
em.emp_id,
em.emp_name,
em.emp_name,
em.emp_wage
from employee em
left join (select e.dept_id,
avg(e.emp_wage) as avg_wage
from employee e group by e.dept_id)
s on s.dept_id = em.dept_id
where em.emp_wage > s.avg_wage
order by em.dept_id;
| dept_id | avg_wage | emp_id | emp_name | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16000.000000 | 1 | 乔峰 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 16000.000000 | 6 | 黄老邪 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 15000.000000 | 3 | 段誉 | 段誉 | 18000.00 |
| 3 | 14000.000000 | 5 | 杨过 | 杨过 | 16000.00 |
| 3 | 14000.000000 | 9 | 金龙法王 | 金龙法王 | 15000.00 |
3、其实上面的结果已经完事了,就是部门名字没出来
select em.dept_id,
d.dept_name,
s.avg_wage,
em.emp_id,
em.emp_name,
em.emp_wage
from employee em
join department d on d.dept_id = em.dept_id
join (select e.dept_id,
avg(e.emp_wage) as avg_wage
from employee e group by e.dept_id)
s on s.dept_id = em.dept_id
where em.emp_wage > s.avg_wage
order by em.dept_id;
| dept_id | dept_name | avg_wage | emp_id | emp_name | emp_wage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广告部 | 16000.000000 | 6 | 黄老邪 | 17000.00 |
| 1 | 广告部 | 16000.000000 | 1 | 乔峰 | 17000.00 |
| 2 | 媒体部 | 15000.000000 | 3 | 段誉 | 18000.00 |
| 3 | 管理部 | 14000.000000 | 5 | 杨过 | 16000.00 |
| 3 | 管理部 | 14000.000000 | 9 | 金龙法王 | 15000.00 |
4、union和 union all 操作符
1、
select语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。同时,每条 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同。2、默认情况下
union操作符已经删除了重复数据。如果允许重复的值,请使用 UNION ALL。
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name1
UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name2
4.1、筛选数据库中不存在的Id
select *
from (
select 10497812 as id
union
select 12190619 as id
union
select 705506 as id
) a
where a.id not in (
select m.id
from table_name m
where m.created_time > '2022-05-12 22:00:00'
)
5、distinct:必须放在开头
create table `test_table`
(
`id` int(11) default '0' comment 'id',
`english` varchar(20) default '' comment 'name',
`age` int(11) default 0
)
INSERT INTO test_table (id, english, age) VALUES (1, 'a', 12);
INSERT INTO test_table (id, english, age) VALUES (2, 'b', 12);
INSERT INTO test_table (id, english, age) VALUES (3, 'c', 13);
INSERT INTO test_table (id, english, age) VALUES (4, 'c', 16);
INSERT INTO test_table (id, english, age) VALUES (5, 'b', 12);
| id | english | age |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 12 |
| 2 | b | 12 |
| 3 | c | 13 |
| 4 | c | 16 |
| 5 | b | 12 |
5.1、 只作用于一个字段
select distinct english from test_table ;
| name |
|---|
| a |
| b |
| c |
5.2、作用于2个字段 :必须得id与name都相同的才会被排除
select distinct english, age from test_table ;
可以观察到排除一个 b 12
| english | age |
|---|---|
| a | 12 |
| b | 12 |
| c | 13 |
| c | 16 |
5.3、count(distinct colume)
select count(english) from test_table ;
5
select count(distinct english) from test_table
3
5.4、distinct 和 count、group by
select age, count( english) from test_table group by age ;
| age | count( english) |
|---|---|
| 12 | 3 |
| 13 | 1 |
| 16 | 1 |
select age, count(distinct english) from test_table group by age ;
| age | count(distinct english) |
|---|---|
| 12 | 2 |
| 13 | 1 |
| 16 | 1 |
六、复杂SQL
1、统计排名
create table scores_tb (
id int auto_increment primary key,
xuehao int not null,
score int not null
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into scores_tb (xuehao,score) values (1001,89),(1002,99),(1003,96),(1004,96),(1005,92),(1006,90),(1007,90),(1008,94);
1)普通排名
SELECT
xuehao,
score,
@curRank := @curRank + 1 AS rank
FROM
scores_tb,
(SELECT @curRank := 0 ) r
ORDER BY
score DESC;
+--------+-------+------+
| XUEHAO | SCORE | RANK |
+--------+-------+------+
| 1002 | 99 | 1 |
| 1003 | 96 | 2 |
| 1004 | 96 | 3 |
| 1008 | 94 | 4 |
| 1005 | 92 | 5 |
| 1006 | 90 | 6 |
| 1007 | 90 | 7 |
| 1001 | 89 | 8 |
+--------+-------+------+
8 rows in set (0.04 sec)
2)分数相同,名次相同,排名无间隔
# 查询语句
SELECT
xuehao,
score,
CASE
WHEN @prevRank = score THEN @curRank
WHEN @prevRank := score THEN @curRank := @curRank + 1
END AS rank
FROM
scores_tb,
( SELECT @curRank := 0, @prevRank := NULL ) r
ORDER BY
score DESC;
+--------+-------+------+
| xuehao | score | rank |
+--------+-------+------+
| 1002 | 99 | 1 |
| 1003 | 96 | 2 |
| 1004 | 96 | 2 |
| 1008 | 94 | 3 |
| 1005 | 92 | 4 |
| 1006 | 90 | 5 |
| 1007 | 90 | 5 |
| 1001 | 89 | 6 |
+--------+-------+------+
8 rows in set (0.05 sec)
3)并列排名,排名有间隔
SELECT
xuehao,
score,
rank
FROM
(SELECT
xuehao,
score,
@curRank := IF( @prevRank = score, @curRank, @incRank ) AS rank,
@incRank := @incRank + 1,
@prevRank := score
FROM
scores_tb,
( SELECT @curRank := 0,
@prevRank := NULL,
@incRank := 1 ) r
ORDER BY score DESC )
s;
+--------+-------+------+
| xuehao | score | rank |
+--------+-------+------+
| 1002 | 99 | 1 |
| 1003 | 96 | 2 |
| 1004 | 96 | 2 |
| 1008 | 94 | 4 |
| 1005 | 92 | 5 |
| 1006 | 90 | 6 |
| 1007 | 90 | 6 |
| 1001 | 89 | 8 |
+--------+-------+------+
8 rows in set (0.06 sec)
4)MySQL 8.0 利用窗口函数实现排名
RANK()OVER
# 三条语句对于上面三种排名
select xuehao,score, ROW_NUMBER() OVER(order by score desc) as row_r from scores_tb;
select xuehao,score, DENSE_RANK() OVER(order by score desc) as dense_r from scores_tb;
select xuehao,score, RANK() over(order by score desc) as r from scores_tb;
# 一条语句也可以查询出不同排名
SELECT xuehao,score,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER w AS 'row_r',
DENSE_RANK() OVER w AS 'dense_r',
RANK() OVER w AS 'r'
FROM `scores_tb`
WINDOW w AS (ORDER BY `score` desc);
# 排名结果
+--------+-------+-------+---------+---+
| xuehao | score | row_r | dense_r | r |
+--------+-------+-------+---------+---+
| 1002 | 99 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1003 | 96 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 1004 | 96 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 1008 | 94 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| 1005 | 92 | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| 1006 | 90 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 1007 | 90 | 7 | 5 | 6 |
| 1001 | 89 | 8 | 6 | 8 |
+--------+-------+-------+---------+---+
2、分组排序
rank() over(partition by ……) as rank_num,
drop table if exists players;
CREATE TABLE `players`
(
`pid` int(2) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`age` int(2) NOT NULL,
`score` int,
PRIMARY KEY (`pid`),
UNIQUE KEY `name` (`name`)
);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (1, 'samual', 25, 98);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (2, 'vino', 20, 96);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (3, 'john', 20, 92);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (4, 'andy', 22, 96);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (5, 'brian', 21, 97);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (6, 'dew', 24, 92);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (7, 'kris', 25, 88);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (8, 'william', 26, 89);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (9, 'george', 23, 88);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (10, 'peter', 19, 88);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (11, 'tom', 20, 92);
INSERT INTO players (pid, name, age, score) VALUES (12, 'andre', 20, 91);
select * from players;
-- 1 2 3 4
select row_number() over (order by age) as rank_num, pid, name, age from players;
-- 1 2 2 4
select dense_rank() over (order by age) as rank_num, pid, name, age from players;
-- 1 2 2 3
select rank() over (order by age) as rank_num, pid, name, age from players;
-- 按照年龄分组
-- 1 2 3 4
select row_number() over(partition by age order by score desc) as rank_num, name,age,score from players;
-- 1 2 2 4
select rank() over(partition by age order by score desc) as rank_num, name, age, score from players;
-- 1 2 2 3
select dense_rank() over(partition by age order by score desc) as rank_num, name,age,score from players;
3、 列互相交换
SELECT q.insuranceid,
q.insurancetype,
q.insurance_sku_code,
q.insurance_sku_type,
if(q.insurance_sku_type = 2, q.insurance_sku_code, q.insuranceid) AS insId,
if(q.insurance_sku_type = 2, q.insuranceid, ifnull(q.insurancetype, '')) AS insType,
SUM(q.premium) AS policyPremium,
COUNT(insuranceid) AS policyNum
FROM qrxpolicy q
WHERE q.created_date >= #{startTime}
AND q.created_date <= #{endTime}
GROUP BY q.insuranceid, q.insurance_sku_code, q.insurance_sku_type
order by insId
4、字符串逗号打平
insurance_ids中只有一个元素(无逗号)或者有多个逗号分隔元素的情况,将其拆分成多行数据。
create table vendor_retain_task
(
`id` bigint unsigned not null auto_increment comment '主键标识列',
`insurance_ids` varchar(32) not null default '' comment '挽留险种,挽留成功放入',
primary key (`id`),
key `idx_created_time` (`created_time`),
key `idx_modified_time` (`modified_time`)
) engine = innodb
default charset = utf8mb4
collate = utf8mb4_bin comment ='';
SELECT
vrt.id,
SUBSTRING_INDEX(SUBSTRING_INDEX(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', numbers.n), ',', -1) AS insurance_id
FROM
vendor_retain_task vrt
JOIN
(
-- 借助 information_schema.columns 生成一个数字序列
SELECT 1 + units.i + tens.i * 10 AS n
FROM
(SELECT 0 i UNION ALL SELECT 1 UNION ALL SELECT 2 UNION ALL SELECT 3 UNION ALL SELECT 4 UNION ALL SELECT 5 UNION ALL SELECT 6 UNION ALL SELECT 7 UNION ALL SELECT 8 UNION ALL SELECT 9) units
JOIN
(SELECT 0 i UNION ALL SELECT 1 UNION ALL SELECT 2 UNION ALL SELECT 3 UNION ALL SELECT 4 UNION ALL SELECT 5 UNION ALL SELECT 6 UNION ALL SELECT 7 UNION ALL SELECT 8 UNION ALL SELECT 9) tens
) numbers
ON
numbers.n <= 1 + (LENGTH(vrt.insurance_ids) - LENGTH(REPLACE(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', '')))
WHERE
SUBSTRING_INDEX(SUBSTRING_INDEX(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', numbers.n), ',', -1) != '';
1、数字序列生成:通过 units 和 tens 两个子查询表进行笛卡尔积操作生成一个 1 - 100 的数字序列(如果 insurance_ids 中元素个数可能超过 100 个,可以扩展此部分),将其作为拆分字符串时的索引。
2、JOIN 条件:numbers.n <= 1 + (LENGTH(vrt.insurance_ids) - LENGTH(REPLACE(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', ''))) 用来确保生成的数字索引不会超过 insurance_ids 中实际元素的数量。LENGTH(vrt.insurance_ids) - LENGTH(REPLACE(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', '')) 计算出字符串中逗号的数量,再加上 1 就是元素的总个数。
3、SUBSTRING_INDEX 函数:内层的 SUBSTRING_INDEX(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', numbers.n) 截取到第 numbers.n 个逗号之前的字符串。外层的 SUBSTRING_INDEX(..., ',', -1) 从内层截取结果中提取最后一个逗号之后的部分,即第 numbers.n 个元素。
4、WHERE 条件:SUBSTRING_INDEX(SUBSTRING_INDEX(vrt.insurance_ids, ',', numbers.n), ',', -1) != '' 过滤掉可能出现的空字符串结果。
八、工具
1、拦截器实现日志打印
1)SqlLogInterceptor
package com.healerjean.proj.config.interceptor;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.CacheKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
/**
* SqlLogInterceptor
*
* @author zhangyujin
* @date 2024/9/23
*/
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class,})})
public class SqlLogInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SqlLogInterceptor.class);
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
String completeSql = "";
try {
log.debug("-------开始执行打印拦截器------");
completeSql = generateSql(invocation);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
log.error("获取sql信息出错,异常信息", e);
} finally {
log.debug("sql执行信息:[{}]", completeSql);
log.debug("-------退出打印拦截器------");
}
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
private String generateSql(Invocation invocation) {
MappedStatement statement = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
Object parameter = null;
if (invocation.getArgs().length > 1) {
parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1];
}
Configuration configuration = statement.getConfiguration();
BoundSql boundSql = statement.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 获取参数对象
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
// 获取参数映射
List<ParameterMapping> params = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
// 获取到执行的SQL
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// SQL中多个空格使用一个空格代替
sql = sql.replaceAll("[\\s]+", " ");
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(params) && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameterObject)) {
// TypeHandlerRegistry 是 MyBatis 用来管理 TypeHandler 的注册器 TypeHandler 用于在 Java 类型和 JDBC 类型之间进行转换
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// 如果参数对象的类型有对应的 TypeHandler,则使用 TypeHandler 进行处理
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(parameterObject)));
} else {
// 否则,逐个处理参数映射
for (ParameterMapping param : params) {
// 获取参数的属性名
String propertyName = param.getProperty();
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
// 检查对象中是否存在该属性的 getter 方法,如果存在就取出来进行替换
if (metaObject.hasGetter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(obj)));
// 检查 BoundSql 对象中是否存在附加参数
} else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
Object obj = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(obj)));
} else {
// SQL匹配不上,带上“缺失”方便找问题
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", "缺失");
}
}
}
}
return sql;
}
private String getParameterValue(Object object) {
String value = "";
if (object instanceof String) {
value = "'" + object + "'";
} else if (object instanceof Date) {
DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.DEFAULT, DateFormat.DEFAULT, Locale.CHINA);
value = "'" + format.format((Date) object) + "'";
} else if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(object)) {
value = object.toString();
}
return value;
}
}
2)拦截器注入
package com.healerjean.proj.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import com.healerjean.proj.config.interceptor.SqlLogInterceptor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.SmartInitializingSingleton;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* mybatisPlusInterceptor
*
* @author zhangyujin
* @date 2023/6/15 11:54.
*/
@Slf4j
@MapperScan("com.healerjean.proj.data.mapper")
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfiguration implements SmartInitializingSingleton {
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().addInterceptor(new SqlLogInterceptor());
}
}
3)日志
2024-09-23 14:22:16 [http-nio-8888-exec-6] DEBUG -[b32e3c76bd3c4799a1382c717159500b] - com.healerjean.proj.config.interceptor.SqlLogInterceptor.intercept[44] - -------开始执行打印拦截器------
2024-09-23 14:22:16 [http-nio-8888-exec-6] DEBUG -[b32e3c76bd3c4799a1382c717159500b] - com.healerjean.proj.config.interceptor.SqlLogInterceptor.intercept[49] - sql执行信息:[SELECT id,name,age,phone,email,valid_flag,start_time,end_time,create_time,update_time FROM user_demo WHERE (name LIKE '%张%')]
2024-09-23 14:22:16 [http-nio-8888-exec-6] DEBUG -[b32e3c76bd3c4799a1382c717159500b] - com.healerjean.proj.config.interceptor.SqlLogInterceptor.intercept[50] - -------退出打印拦截器------