今日算法之_42_组合总和
前言
Github:https://github.com/HealerJean
1、组合总和1
给定一个无重复元素的数组
candidates和一个目标数target,找出candidates中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
1.1、解题思路
根据示例 1:输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7],target = 7。
候选数组里有 2 ,如果找到了 7 - 2 = 5 的所有组合,再在之前加上 2 ,就是 7 的所有组合;
同理数组里有 3, 如果找到了 7 - 3 = 4 的所有组合,再在之前加上 3 ,就是 7 的所有组合,依次这样找下去;
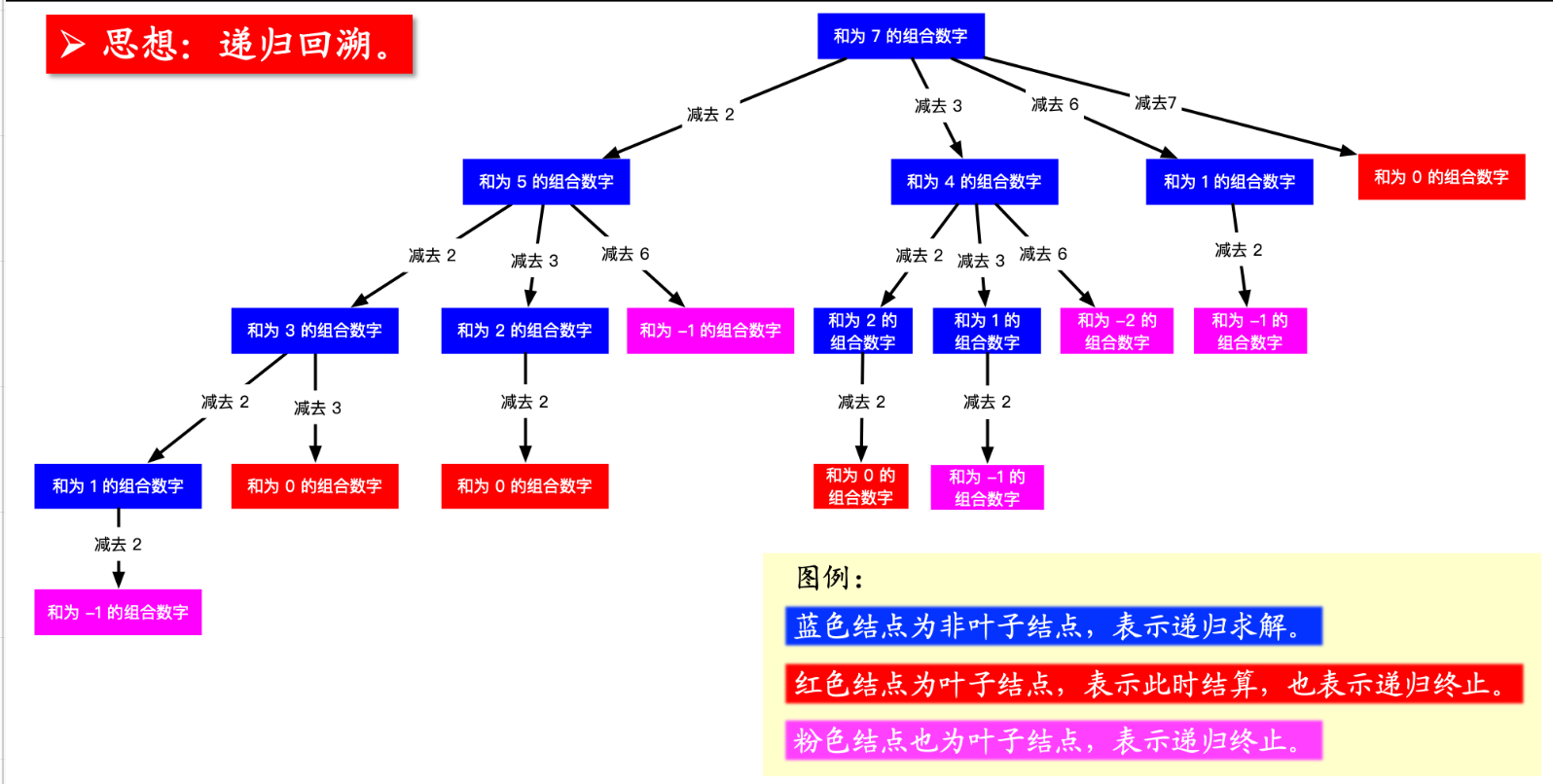
上面的思路就可以画成下面的树形图。
1.1.1、回溯法
蓝色结点表示:尝试找到组合之和为该数的所有组合,怎么找呢?逐个减掉候选数组中的元素即可;
以 target = 7 为根结点,每一个分支做减法;
减到 0 或者负数的时候,到了叶子结点;
减到 0 的时候结算,这里 “结算” 的意思是添加到结果集;
从根结点到叶子结点(必须为 0)的路径,就是题目要我们找的一个组合。
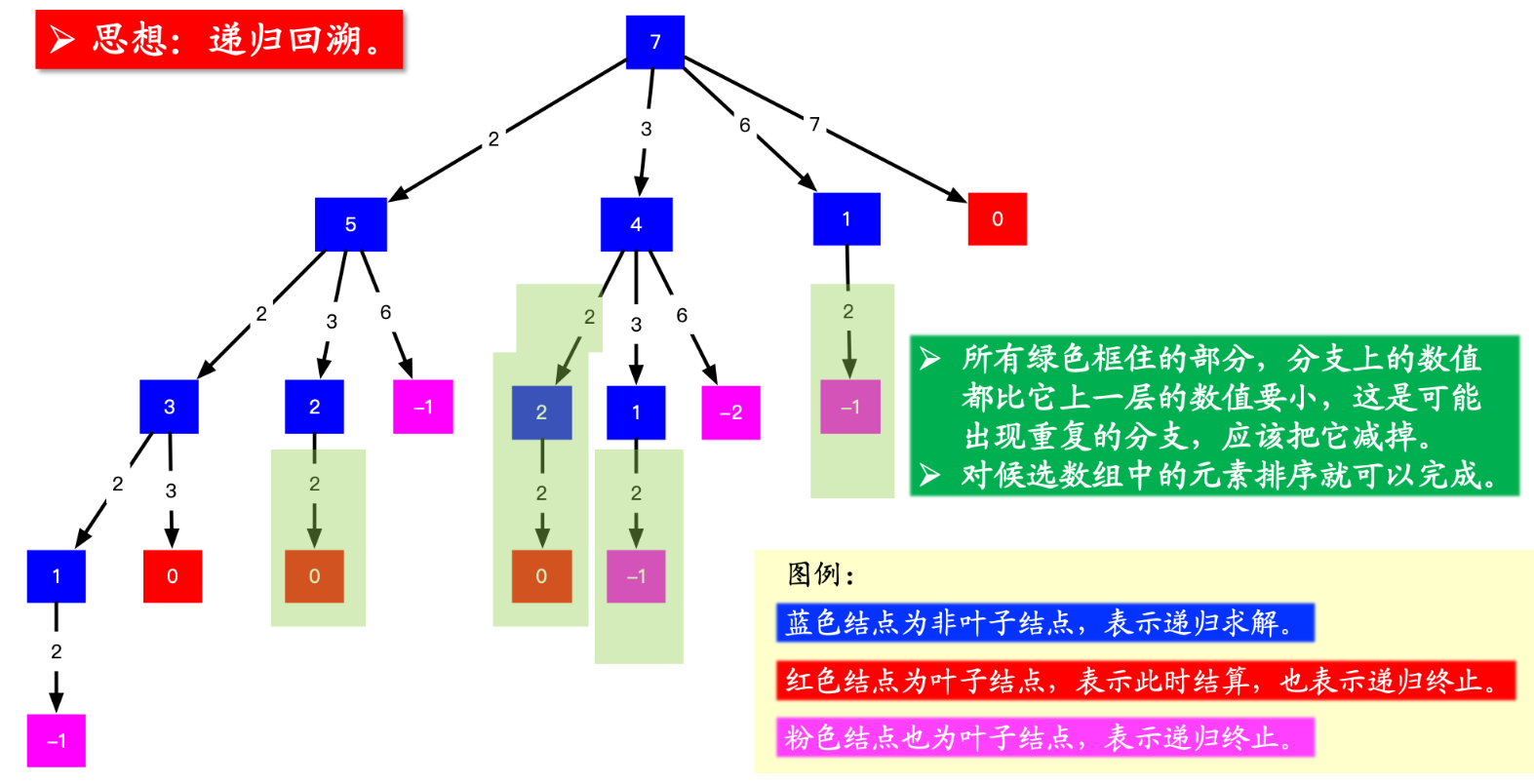
1.1.2、去重
画出图以后结果有 4 个 0,对应的路径是 [[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]],而示例中的解集只有 [[7], [2, 2, 3]],很显然,重复的原因是在较深层的结点值考虑了之前考虑过的元素
1、在搜索的时候,需要设置搜索起点的下标 begin ,由于一个数可以使用多次,下一层的结点从这个搜索起点开始搜索;
2、在搜索起点 begin 之前的数因为以前的分支搜索过了,所以一定会产生重复。
1.2、算法
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
// 排序是为了提前终止搜索,当然也不可以不排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
dfs(target, 0, stack, candidates, res);
return res;
}
/**
* 深度遍历
*/
public void dfs(int target, int index, Stack<Integer> stack, int[] candidates, List<List<Integer>> res) {
//等于零说明结果符合要求,将栈里面的数据取出来放到结果List中去
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
//遍历,index为本分支上一节点的减数的下标,只往后看不往回看这样就不会有重复的了,类似于3数之和
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
//如果减数大于目标值,则差为负数,不符合结果
if (candidates[i] <= target) {
stack.push(candidates[i]);
//目标值减去元素值,
dfs(target - candidates[i], i, stack, candidates, res);
//如果能走到这里,说明回溯已经完成了,但是却没有结果,所以要回退到上一个节点,或者去重。具体debug一遍就知道了
stack.pop();
}
}
}
1.3、测试
@Test
public void test() {
int[] candidates = {2, 3, 6, 7};
int target = 7;
System.out.println(combinationSum(candidates, target));
}
[[2, 2, 3], [7]]
2、组合总和2
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
所求解集为:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
1.1、解题思路
和上面 的有些类似,再加一点全排列2的知识
1.2、算法
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
//先排序,提前终止搜索
Arrays.sort(candidates);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[candidates.length];
dfs(target, 0, stack, candidates, res, used );
return res;
}
public void dfs(int target, int index, Stack<Integer> stack, int[] candidates, List<List<Integer>> res, boolean[] used ) {
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
//必须保证是不同一层
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1] && !used[i-1] ){
continue;
}
if (candidates[i] <= target) {
stack.push(candidates[i]);
used[i] = true ;
dfs(target - candidates[i], i +1, stack, candidates, res, used);
stack.pop();
used[i] = false ;
}
}
}
1.3、测试
@Test
public void test() {
int[] candidates = {10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5};
int target = 8;
System.out.println(combinationSum2(candidates, target));
}
3、组合总和3
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
说明:所有数字都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]
示例 2:
示例 2:
输入: k = 3, n = 9
输出: [[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]
1.1、解题思路
和上面 的有些类似,再加一点全排列2的知识
1.2、算法
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
//先排序,提前终止搜索
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
dfs(1,n, k, stack, res);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int index, int target, int k, Stack<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// 满足 数量为 k , 和为 n(target)
if (stack.size() == k && target == 0 ) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <= 9; i++) {
if (i <= target) {
stack.push(i);
dfs(i + 1, target - i,k, stack, res);
stack.pop();
}
}
}
1.3、测试
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println(combinationSum3(2, 18));
}