今日算法之_12_二叉树遍历
前言
Github:https://github.com/HealerJean
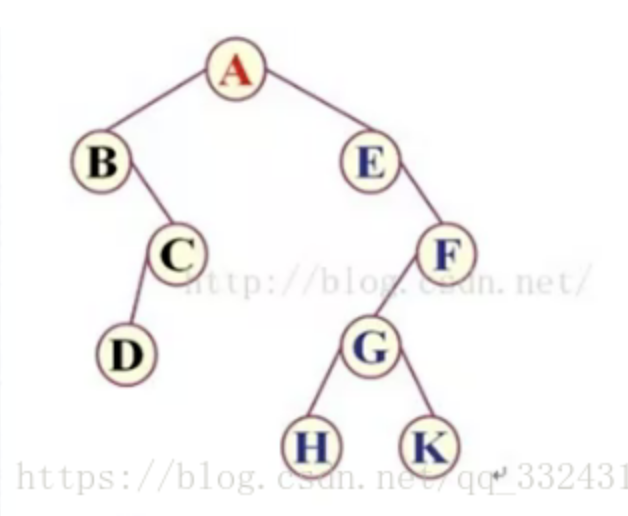
1、二叉树遍历
先序遍历 ,中序遍历,后序遍历,层序遍历
/**
* 打印节点数值
*/
public static void printNode(Node node) {
System.out.print(node.getData()+ " ");
}
/**
* 初始化二叉树:
* 必须逆序简历,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子节点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化得,不逆序建立会报错
*/
public static Node init() {
Node H = new Node("H", null, null);
Node K = new Node("K", null, null);
Node G = new Node("G", H, K);
Node F = new Node("F", G, null);
Node E = new Node("E", null, F);
Node D = new Node("D", null, null);
Node C = new Node("C", D, null);
Node B = new Node("B", null, C);
Node A = new Node("A", B, E);
return A;
}
@Data
public static class Node {
private String data;
private Node leftNode;
private Node rightNode;
public Node(String data, Node leftNode, Node rightNode) {
this.data = data;
this.leftNode = leftNode;
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
}
1.1、先序遍历(根 左 右)
A B C D E F G H K
1.1.1、递归实现
1.1.1.1、算法
/**
* 先序遍历(根左右):递归
*/
public void preOrder(Node root) {
//1、打印根节点
printNode(root);
//2、使用递归遍历左孩子
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
preOrder(root.getLeftNode());
}
//3、使用递归遍历右孩子
if (root.getRightNode() != null) {
preOrder(root.getRightNode());
}
}
1.1.1.2、测试
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("先序遍历");
Node node = init();
preOrder(node);
}
1.1.2、非递归实现 (栈)
1.1.2.1、解题思路
根据栈的特性:后进先出,先进后出:
1、因为初次打印就是跟节点,所以每次节点进来,不管三七二十一先打印跟节点,然后根节点入栈,再讲节点切换为左子树节点作为根节点,循环,直到左子树为空
2、这个时候栈中有数据的,也就是说所有靠右的节点的集合
如果右子树不为空,然后获取最后进入的节点的右子树作为根节点再进行1中的遍历。
如果右子树为空,则从栈中取出数据继续执行2
1.1.2.2、算法
/**
* 先序遍历(根左右):非递归
* 思想:栈的解决方式(后进先出,先进后出)
*/
public static void preStack(Node node) {
// 1、初始化一个栈
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
// 2、判断节点不为NULL,或者栈不为空
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// if (node != null) { 目的是为了打压跟节点和左子树
if (node != null) {
//先打印跟节点
printNode(node);
//根节点放入 栈中,放到栈中的目的
stack.push(node);
//设置循环节点为当前节点的左子树
node = node.getLeftNode();
//目的是为了从栈里面取出节点
} else {
node = stack.pop();
//设置循环节点为当前节点的右子树
node = node.getRightNode();
}
}
}
1.1.2.3、测试
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("先序遍历");
Node node = init();
System.out.println();
preStack(node);
}
1.2、中序遍历(左 根 右)
B D C A E H G K F
1.2.1、递归实现
1.2.1.1、算法
/**
*
* 中序遍历(左根右) :递归
*/
public void inOrder(Node root) {
//使用递归遍历左孩子
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
inOrder(root.getLeftNode());
}
//打印根节点
printNode(root);
//使用递归遍历右孩子
if (root.getRightNode() != null) {
inOrder(root.getRightNode());
}
}
1.2.1.2、测试
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("中序遍历");
Node node = init();
inOrder(node);
}
1.2.2、非递归实现 (栈)
1.2.2.1、解题思路
栈的特性:后进先出,先进后出
1、因为初次打印就是左节点,所以我们需要讲右面的节点全部入栈,知道左子树为空
2、这个时候栈里面有数据了,出栈,直接打印根节点,然后获取右子树。
如果右子树不为空,讲当前节点设置为 则执行1,继续获取所有的节点,并入栈
如果右子树为空, 则继续执行2,打印节点即可
1.2.2.2、算法
/**
* 中序遍历(左根右) :非递归
* 栈的解决方式:后进先出,先进后出
*/
public void inStack(Node node) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (node != null) {
//后进先出,讲所有的左子树和跟节点依次放入
stack.push(node);
node = node.getLeftNode();
}
//消化队列中的数据
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
printNode(node);
node = node.getRightNode();
}
}
}
1.2.2.3、测试
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("中序遍历");
Node node = init();
inStack(node);
}
1.3、后序遍历(左 右 根 )
D C B H K G F E A
1.3.1、递归实现
1.3.1.1、算法
/**
*
* 后续遍历(左右根) :递归
*/
public static void postOrder(Node root) {
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
postOrder(root.getLeftNode());
}
if (root.getRightNode() != null) {
postOrder(root.getRightNode());
}
printNode(root);
}
1.2.1.2、测试
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("中序遍历");
Node node = init();
postOrder(node);
}
1.4、层序遍历
A E B F C G D K H
1.4.1、解题思路 :队列
队列的解决方案,先进先出
将每一行的数据放到队列中,依次打印出来
1.4.2、算法
/**
* 层序遍历(上到下,从从右到左):
* 队列的解决方案,先进先出
*/
public static void rightToLeft(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//表示每行有多少个
int hangSize = queue.size();
//遍历每行的数据
while (hangSize > 0) {
//从队列中取出,打印根节点
Node node = queue.remove();
printNode(node);
hangSize--;
if (node.getRightNode() != null) {
queue.add(node.getRightNode());
}
if (node.getLeftNode() != null) {
queue.add(node.getLeftNode());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 层序遍历(上到下,从从左到右):
* 队列的解决方案,将每一行的数据放到队列中,依次打印出来
*/
public void leftToRigit(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = queue.size();
while (i > 0) {
Node node = queue.remove();
printNode(node);
i--;
if (node.getLeftNode() != null) {
queue.add(node.getLeftNode());
}
if (node.getRightNode() != null) {
queue.add(node.getRightNode());
}
}
}
}
1.4.3、测试
@Test
public void test() {
Node root = init();
System.out.println("层序遍历 从上到下,从右到左");
rightToLeft(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("层序遍历 从上到下,从左到右");
leftToRigit(root);
}
层序遍历 从上到下,从右到左
A E B F C G D K H
层序遍历 从上到下,从左到右
A B E C F D G H K
1.5、之字形遍历
1.5.1、解题思路:队列
1.5.2、算法
1.5.3、测试