文件File详解
前言
Github:https://github.com/HealerJean
一、文件简介
在 Java 中操作文件的方法本质上只有两种:字符流和字节流,而字节流和字符流的实现类又有很多,因此在文件写入时我们就可以选择各种各样的类来实现。我们本文就来盘点一下这些方法,顺便测试一下它们性能,以便为我们选出最优的写入方法。
1、什么是流
Java中的“流”是一种抽象的概念,也是一种比喻,就好比水流一样,水流是从一端流向另一端的,而在Java中的“水流”就是数据,数据会从一端“流向”另一端。根据流的方向性,我们可以将流分为 输入流和输出流
⬤ 当程序需要从数据源中读入数据的时候就会开启一个输入流
⬤ 写出数据到某个数据源目的地的时候也会开启一个输出流,数据源可以是文件、内存或者网络等。
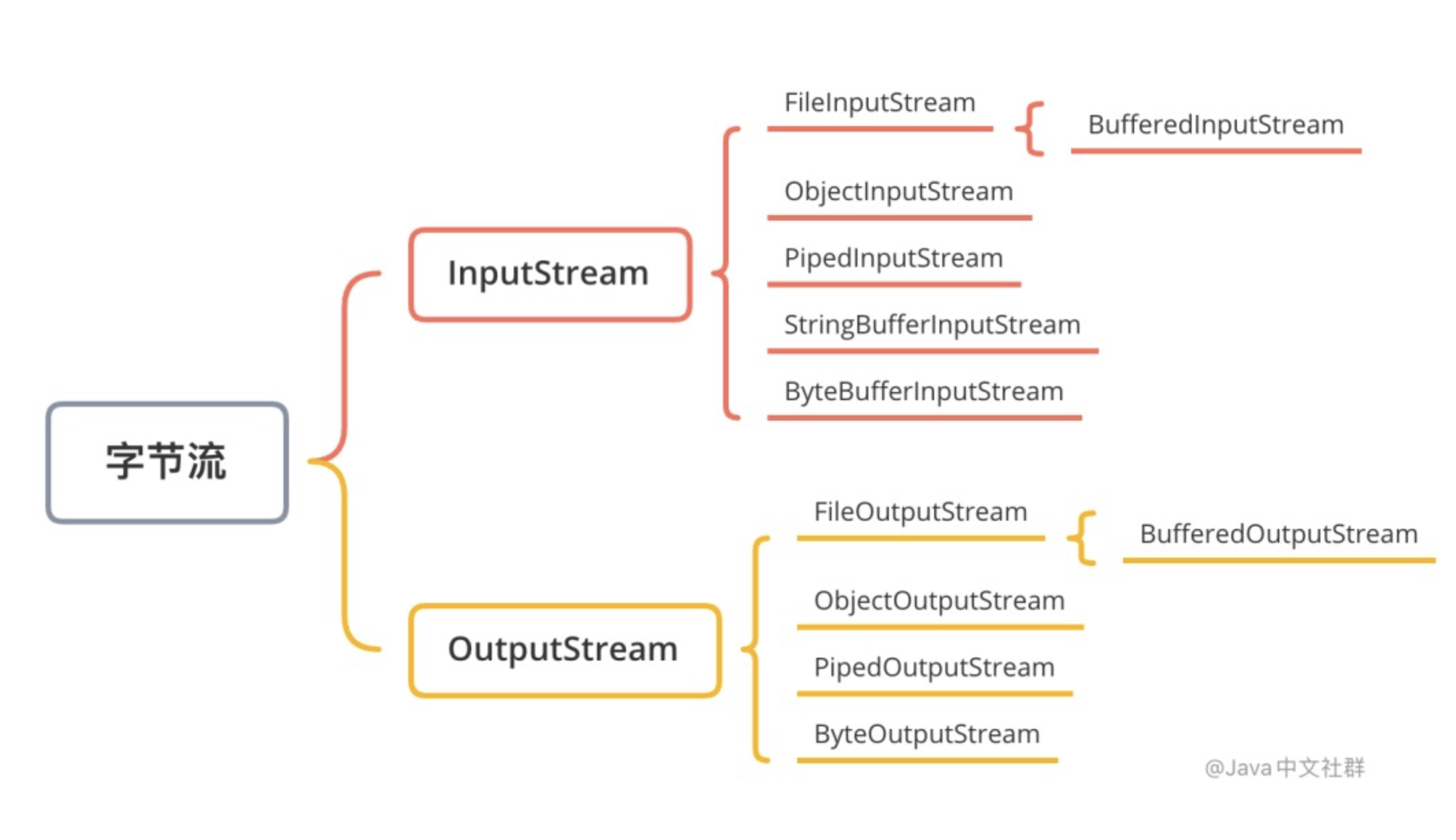
2、什么是字节流
字节流的基本单位为字节(
Byte),一个字节通常为8位,它是用来处理二进制(数据)的。字节流有两个基类,其中InputStream用于读操作,而OutputStream用于写操作。:⬤
InputStream(输入字节流)⬤
OutputStream(输出字节流)。
3、什么是字符流?
字符流的基本单位为
Unicode,大小为两个字节(Byte),它通常用来处理文本数据。字符流的两个基类:⬤
Reader(输入字符流)⬤
Writer(输出字符流)。
4、流的分类
流可以根据不同的维度进行分类,比如可以根据流的方向进行分类,也可以根据传输的单位进行分类,还可以根据流的功能进行分类,比如以下几个。
1)按流向分类
⬤ 输出流:OutputStream 和 Writer 为基类。
⬤ 输入流:InputStream 和 Reader 为基类。
2)根据传输数据单位分类
我们通常是以传输数据的单位来为流进行分类。
⬤ 字节流:OutputStream 和 InputStream 为基类。
⬤ 字符流:Writer 和 Reader 为基类。
3)根据功能分类
⬤ 字节流:可以从或向一个特定的地方(节点)读写数据。
⬤ 处理流:是对一个已存在的流的连接和封装,通过所封装的流的功能调用实现数据读写。
4)写文件的6种方法
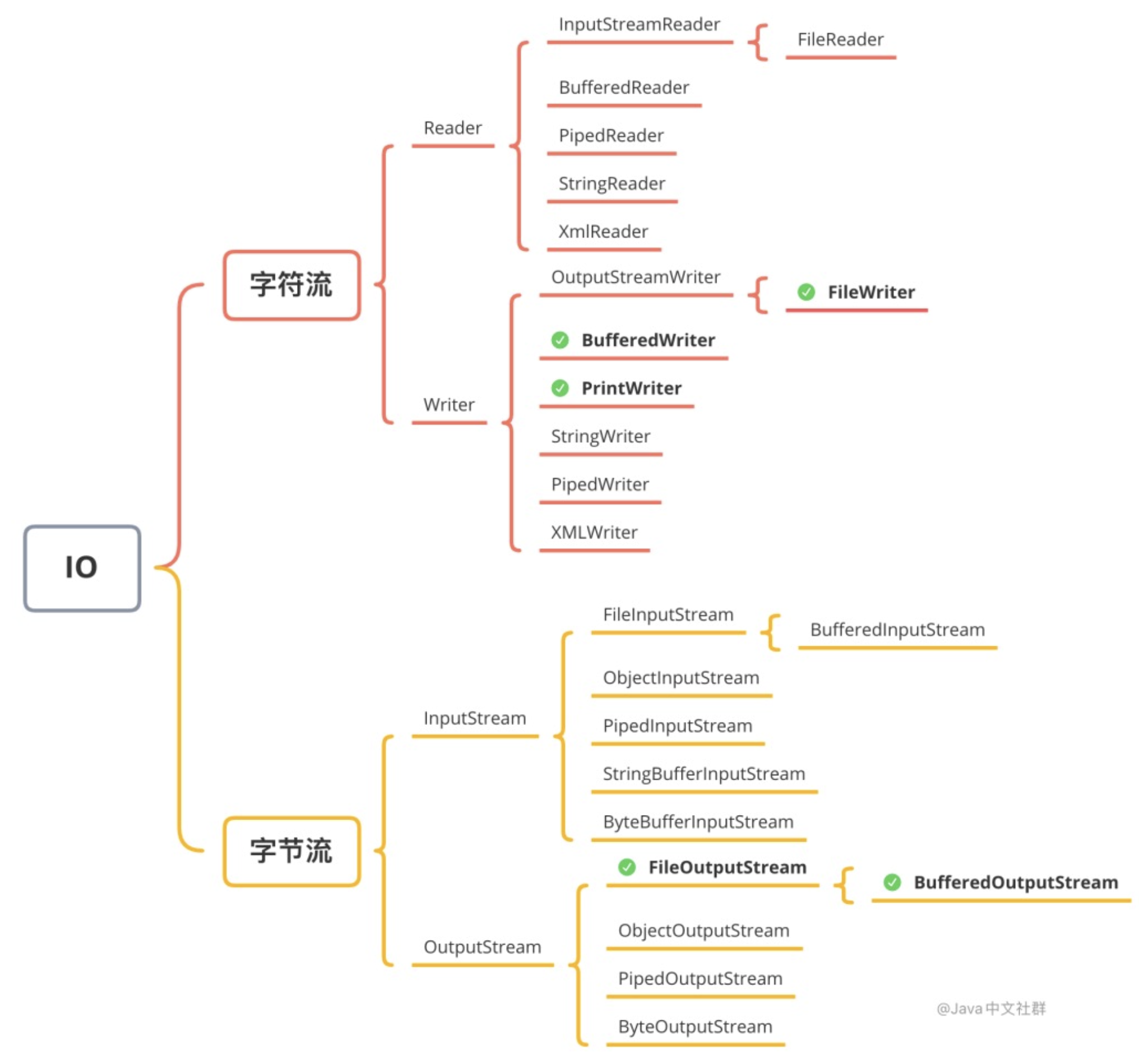
a、FileWriter
FileWriter属于「字符流」体系中的一员,也是文件写入的基础类,它包含5个构造函数,可以传递一个具体的文件位置,或者File对象,第二参数表示是否要追加文件,默认值为false表示重写文件内容,而非追加文件内容(关于如何追加文件,我们后面会讲)。
/**
* 方法 1:使用 FileWriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void fileWriterMethod(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(filepath)) {
fileWriter.append(content);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
fileWriterMethod("/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write1.txt", "哈喽,Java中文社群.");
}
b、BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter也属于字符流体系的一员,与FileWriter不同的是BufferedWriter自带缓冲区,因此它写入文件的性能更高
小知识点:缓冲区 缓冲区又称为缓存,它是内存空间的一部分。也就是说,在内存空间中预留了一定的存储空间,这些存储空间用来缓冲输入或输出的数据,这部分预留的空间就叫做缓冲区。
缓冲区的优势:以文件流的写入为例,如果我们不使用缓冲区,那么每次写操作 CPU 都会和低速存储设备也就是磁盘进行交互,那么整个写入文件的速度就会受制于低速的存储设备(磁盘)。但如果使用缓冲区的话,每次写操作会先将数据保存在高速缓冲区内存上,当缓冲区的数据到达某个阈值之后,再将文件一次性写入到磁盘上。因为内存的写入速度远远大于磁盘的写入速度,所以当有了缓冲区之后,文件的写入速度就被大大提升了。
/**
* 方法 2:使用 BufferedWriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void bufferedWriterMethod(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filepath))) {
bufferedWriter.write(content);
}
}
c、PrintWriter
PrintWriter也属于字符流体系中的一员,它虽然叫“字符打印流”,但使用它也可以实现文件的写入,实现代码如下:从上述代码可以看出,无论是
PrintWriter还是BufferedWriter都必须基于FileWriter类来完成调用。
/**
* 方法 3:使用 PrintWriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void printWriterMethod(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(filepath))) {
printWriter.print(content);
}
}
d、FileOutputStream
上面 3 个示例是关于字符流写入文件的一些操作,而接下来我们将使用字节流来完成文件写入。我们将使用
String自带的getBytes()方法先将字符串转换成二进制文件,然后再进行文件写入,它的实现代码如下:
/**
* 方法 4:使用 FileOutputStream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void fileOutputStreamMethod(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filepath)) {
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
}
e、BufferedOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream属于字节流体系中的一员,与FileOutputStream不同的是,它自带了缓冲区的功能,因此性能更好,它的实现代码如下:
/**
* 方法 5:使用 BufferedOutputStream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void bufferedOutputStreamMethod(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(filepath))) {
bufferedOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}
}
f、Files
接下来的操作方法和之前的代码都不同,接下来咱们就使用 JDK 7 中提供的一个新的文件操作类
Files来实现文件的写入。
Files类是JDK 7添加的新的操作文件的类,它提供了提供了大量处理文件的方法,例如文件复制、读取、写入,获取文件属性、快捷遍历文件目录等,这些方法极大的方便了文件的操作,它的实现代码如下:
/**
* 方法 6:使用 Files 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void filesTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
Files.write(Paths.get(filepath), content.getBytes());
}
5)性能测试
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class WriteExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 构建写入内容
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
stringBuilder.append("ABCDEFGHIGKLMNOPQRSEUVWXYZ");
}
// 写入内容
final String content = stringBuilder.toString();
// 存放文件的目录
final String filepath1 = "/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write1.txt";
final String filepath2 = "/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write2.txt";
final String filepath3 = "/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write3.txt";
final String filepath4 = "/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write4.txt";
final String filepath5 = "/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write5.txt";
final String filepath6 = "/Users/mac/Downloads/io_test/write6.txt";
// 方法一:使用 FileWriter 写文件
long stime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
fileWriterTest(filepath1, content);
long etime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("FileWriter 写入用时:" + (etime1 - stime1));
// 方法二:使用 BufferedWriter 写文件
long stime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
bufferedWriterTest(filepath2, content);
long etime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("BufferedWriter 写入用时:" + (etime2 - stime2));
// 方法三:使用 PrintWriter 写文件
long stime3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
printWriterTest(filepath3, content);
long etime3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("PrintWriterTest 写入用时:" + (etime3 - stime3));
// 方法四:使用 FileOutputStream 写文件
long stime4 = System.currentTimeMillis();
fileOutputStreamTest(filepath4, content);
long etime4 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("FileOutputStream 写入用时:" + (etime4 - stime4));
// 方法五:使用 BufferedOutputStream 写文件
long stime5 = System.currentTimeMillis();
bufferedOutputStreamTest(filepath5, content);
long etime5 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("BufferedOutputStream 写入用时:" + (etime5 - stime5));
// 方法六:使用 Files 写文件
long stime6 = System.currentTimeMillis();
filesTest(filepath6, content);
long etime6 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Files 写入用时:" + (etime6 - stime6));
}
/**
* 方法六:使用 Files 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void filesTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
Files.write(Paths.get(filepath), content.getBytes());
}
/**
* 方法五:使用 BufferedOutputStream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void bufferedOutputStreamTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(filepath))) {
bufferedOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}
}
/**
* 方法四:使用 FileOutputStream 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void fileOutputStreamTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filepath)) {
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
}
/**
* 方法三:使用 PrintWriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void printWriterTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(filepath))) {
printWriter.print(content);
}
}
/**
* 方法二:使用 BufferedWriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void bufferedWriterTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filepath))) {
bufferedWriter.write(content);
}
}
/**
* 方法一:使用 FileWriter 写文件
* @param filepath 文件目录
* @param content 待写入内容
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void fileWriterTest(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(filepath)) {
fileWriter.append(content);
}
}
}
在查看结果之前,我们先去对应的文件夹看看写入的文件是否正常,如下图所示:

从上述结果可以看出,每种方法都正常写入了 26 MB 的数据,它们最终执行的结果如下图所示:
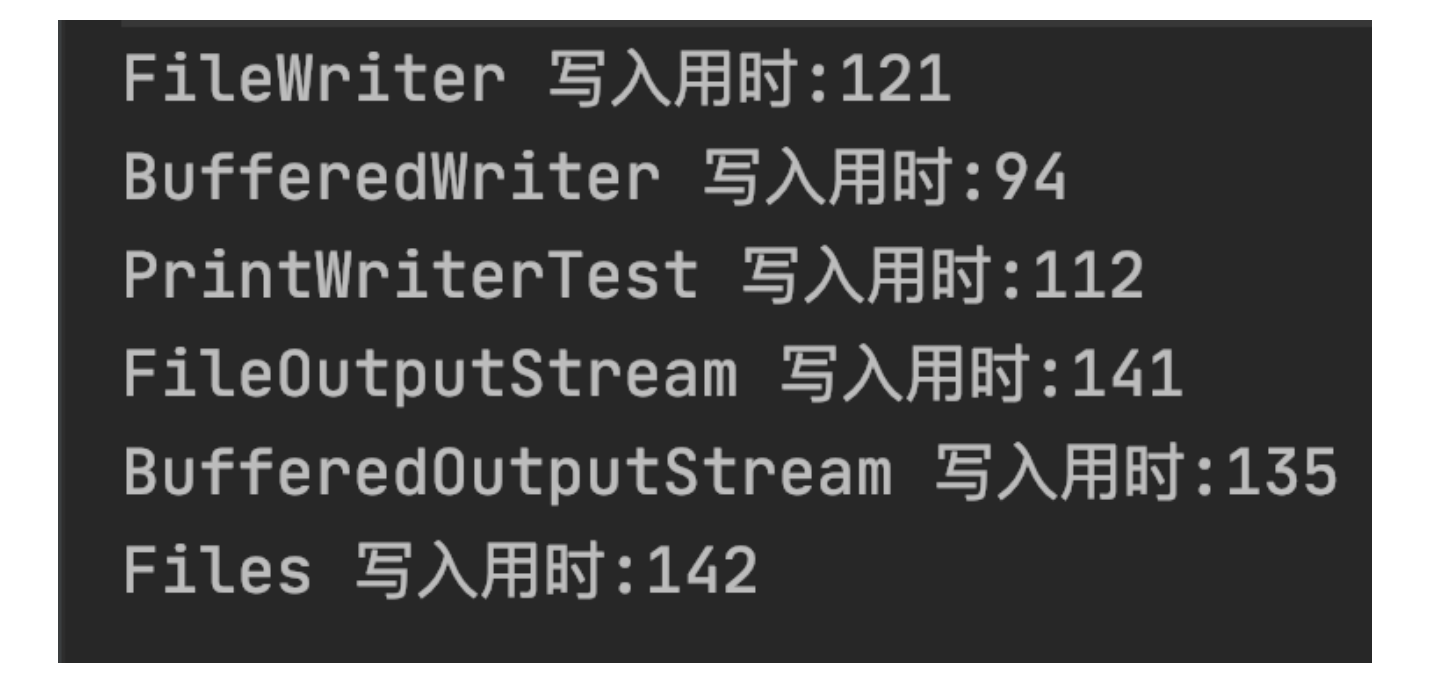
总结:从以上结果可以看出,字符流的操作速度最快,这是因为我们本次测试的代码操作的是字符串,所以在使用字节流时,需要先将字符串转换为字节流,因此在执行效率上不占优势。
6)内容追加
以上代码会对文件进行重写,如果只想在原有的基础上追加内容,就需要在创建写入流的时候多设置一个
append的参数为true,比如如果我们使用FileWriter来实现文件的追加的话,实现代码是这样的:
public static void fileWriterMethod(String filepath, String content) throws IOException {
// 第二个 append 的参数传递一个 true = 追加文件的意思
try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(filepath, true)) {
fileWriter.append(content);
}
}
5)总结
本文我们展示了 6 种写入文件的方法,这 6 种方法总共分为 3 类:字符流写入、字节流写入和
Files类写入。其中操作最便利的是
Files类,但它的性能不怎么好。如果对性能有要求就推荐使用带有缓存区的流来完成操作,如BufferedWriter或BufferedOutputStream。如果写入的内容是字符串的话,那么推荐使用BufferedWriter,如果写入的内容是二进制文件的话就推荐使用BufferedOutputStream。
二、文件基本操作
1、创建文件
1、路径不存在,fileNameTxt.createNewFile() 会抛出异常
2、只有路径,不会创建出文件,也不会报错,无法创建
3、路径存在,文件不存在,创建成功
4、没有路径,只有文件文件名,和则创建的文件和src一个级别,创建成功
/**
* 1、路径不存在,fileNameTxt.createNewFile() 会抛出异常
* 2、只有路径,不会创建出文件,也不会报错,无法创建,但是不会报错
* 3、路径存在,文件不存在,创建成功
* 4、没有路径,只有文件文件名,和则创建的文件和src一个级别,创建成功
*/
@Test
public void createFile() throws IOException {
String filePath = "newFile.txt";
File fileNameTxt = new File(filePath);
if (!fileNameTxt.exists()) {
fileNameTxt.createNewFile();
}
log.info("创建成功");
}
/**
* 2、创建有目录的文件:通过父的目录引入文件 directoryName 是父类
*/
@Test
public void createHavaDirectoryFile() throws IOException {
String directoryName = "D:/test/file/d02_createHavaDirectoryFile";
String fileName = "directoryName.txt";
File directoryNameTxt = new File(directoryName, fileName);
if (!directoryNameTxt.exists()) {
directoryNameTxt.createNewFile();
}
log.info("创建有目录的文件成功");
}
2、判断文件、目录
/**
* 3、 判断文件、目录
*/
@Test
public void judgeFileOrDirectory() {
File file = new File("D:/test/file/d02_createHavaDirectoryFile");
log.info("测试开始");
if (file.isFile()) {
log.info(file.getPath() + "是一个文件");
} else if (file.isDirectory()) {
log.info(file.getPath() + "是一个目录");
} else {
log.info(file.getPath() + "不是文件也不是目录");
}
}
3、创建目录
创建目录,即使路径不存在,也会创建相关路径,因为是
mkdirs
/**
* 3、创建目录
* 判断是不是目录
* 创建目录,即使路径不存在,也会创建相关路径,因为是mkdirs
*/
@Test
public void createDirectory() {
//引入目录
File directoryName = new File("D:/test/healerjean/file");
if (!directoryName.exists()) {
directoryName.mkdirs();
log.info(directoryName.getPath() + "创建目录成功");
}
}
4、普通复制文件
第一个文件以及路径必须存在, 否则
fileInputStream会报错第二个文件可以不存在,但是路径必须存在,如果路径不存在则
new FileOutputStream会报错
/**
* 5、复制文件
* Input第一个文件以及路径必须存在, 否则 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outFilePath); FileNotFoundException 异常
* Output第二个文件可以不存在,但是路径必须存在,如果路径不存在则FileOutSteam会报错
*/
public void copyFile() throws IOException {
String inFilePath = "D:/test/file/d03_copyFile/exist/file.txt";
String outFilePath = "D:/test/file/d03_copyFile/no_exist/newfile.txt";
FileInputStream ins = new FileInputStream(inFilePath);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outFilePath);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int n = 0;
while ((n = ins.read(b)) != -1) {
out.write(b, 0, n);
}
ins.close();
out.close();
log.info("复制文件成功");
}
5、递归目录
1)递归整个目录
file.listFiles()是获取file这个对象也就是file这个目录下面的文件和文件夹的集合
/**
* 6、递归遍历整个目录的文件
* file.listFiles()是获取file这个对象也就是file这个目录下面的文件和文件夹的集合
*/
public void cycleFiles(File file) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File sonFile : files) {
if (sonFile.isDirectory()) {
cycleFiles(sonFile);
} else {
log.info(sonFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
log.info(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
@Test
public void testCycleFiles() {
File file = new File("D:/test");
cycleFiles(file);
}
2) 递归递归整个目录,并读取文件内容进行匹配
/**
* 6.2 、递归目录,读取文件内容进行匹配
* size :用于保留统计记录的个数
*/
private static int size = 1;
public void cycleFileContent(File file, String content) throws Exception {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {
cycleFileContent(f, content);
} else {
String path = f.getPath();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(f);
ByteArrayOutputStream outStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
outStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
String str = new String(outStream.toByteArray(), "utf-8");
if (str.contains(content)) {
log.info("第【{}】个文件匹配到内容,路径为:{}", size, f.getPath());
size++;
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void testCycleFileContent() throws Exception {
File file = new File("D:/test");
String content = "co";
cycleFileContent(file, content);
}
6、读取文件内容
1)读取整个文件内容,
转化为ByteArrayOutputStream读取
/**
* 7.1、读取文件内容:转化为ByteArrayOutputStream读取
*/
@Test
public void readFileContent() throws Exception {
File file = new File("D:\\test\\file\\file.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int len = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
byteOutputStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
String txtValue = new String(byteOutputStream.toByteArray(), "utf-8");
log.info(txtValue);
}
2)一行一行读取文件内容
@Test
public void readFileLineContent() throws Exception {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/logs/hlj-log4j.log");
InputStreamReader inputReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputReader);
String lineContent = null;
int line = 0;
while ((lineContent = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
line++;
log.info("第【{}】行的内容为:{}", line, lineContent);
}
}
7、根据字符串生成内容
/**
* 8、根据内容生成文件
*/
@Test
public void contentToFile() throws Exception {
String content = "我是大好人";
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "") + ".txt";
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/test/" + fileName);
byte[] buffer = content.getBytes("utf-8");
outputStream.write(buffer);
log.info("文件【{}】创建成功", fileName);
outputStream.close();
}
8、局域网文件调用
File file = new File("//192.168.31.1/file");
9、临时目录
/**
* 9、File.createTempFile 所在目录 C:\Users\HealerJean\AppData\Local\Temp
* 注意:1、 prefix必须大于3个字符,2、suffix需要带上 . , 比如:.png、.zip
*
*/
@Test
public void test() {
try {
//创建文件 a_name.4788216370145255403.jpg ,中间是随机生成的
// File jpgFile = File.createTempFile("a_name.", ".jpg");
//创建目录 scf.contract.4137975757793800315.dir
File directory = File.createTempFile("scf.contract.", ".dir");
directory.delete();
directory.mkdirs();
//指定目录中创建文件
File pdfFile = File.createTempFile("scf.contract.", ".pdf", new File("C:\\Users\\HealerJean\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\healerjean"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
三、上传下载
1、上传
@ApiOperation(
value = "文件上传",
notes = "文件上传",
consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE,
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE,
response = String.class)
@PostMapping(value = "upload", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public String upload(MultipartFile file) {
log.info("文件管理--------文件上传--------请求参数{}", file);
//1、确定文件存储目录
String javaIoTmpdir = System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir");
File tempFile = new File(javaIoTmpdir);
if (!tempFile.exists()) {
tempFile.mkdirs();
}
// 2、文件上传
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
File outFile = new File(tempFile, fileName);
// InputStream inputStream = null;
// FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
// 1、inputstream -> 本地文件
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(file.getInputStream(), outFile);
// 2、MultipartFile文件 -> 本地文件
// file.transferTo(outFile);
// 3、MultipartFile 文件获取字节 -> OutputStream
// byte[] bytes = file.getBytes();
// fileOutputStream = (new FileOutputStream(outFile));
// fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
// 4、InputStream -> OutputStream
// inputStream = file.getInputStream();
// fileOutputStream = (new FileOutputStream(outFile));
// IOUtils.copy(inputStream, fileOutputStream);
log.info("文件管理--------文件上传成功--------上传文件名{}", file.getOriginalFilename());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.info("文件上传失败");
throw new RuntimeException("文件上传失败", e);
} finally {
log.info("准备开始关闭流");
// try {
// if (fileOutputStream != null) {
// fileOutputStream.close();
// }
// } catch (IOException e) {
// log.error("流关闭失败", e);
// }
// try {
// if (inputStream != null) {
// inputStream.close();
// }
// } catch (IOException e) {
// log.error("流关闭失败", e);
// }
}
return fileName;
}
2、下载
@ApiOperation(
value = "文件下载",
notes = "文件下载",
consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE,
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE,
response = String.class)
@GetMapping(value = "download/{fileName}", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public void downLoad(HttpServletResponse response, @PathVariable String fileName, Boolean preview) {
InputStream inputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
log.info("文件管理--------文件下载--------请求参数{}", fileName);
String javaIoTmpdir = System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir");
File file = new File(javaIoTmpdir, fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
throw new BusinessException("文件不存在");
}
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
if (preview != null && !preview) {
//强制浏览器下载
log.info("文件管理--------强制浏览器下载--------文件名{}", fileName);
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
} else {
log.info("文件管理--------文件预览--------文件名{}", fileName);
//浏览器尝试打开,支持office online或浏览器预览pdf功能
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "inline;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
}
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("文件:{},下载失败", fileName, e);
throw new RuntimeException("文件上传失败", e);
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("inputStream未正确关闭");
}
}
if (outputStream != null) {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("outputStream未正确关闭");
}
}
}
}
3、多个文件上传
@Transient
private String attachPics;
@Transient
private String attachFileNames;
@Transient
private String attachFileTypes;
@Transient
private List<OldBackGroundBalanceTransferUserAttachment> attachmentList;
@Override
public void saveOldBackGroundBalanceTransferUser(Long adminId, OldBackGroundBalanceTransferUser data) {
data.setAdminId(adminId);
data.setAuditStatus(EnumOldBackGroundBalanceTranferStatus.待审核.status);
OldBackrUser tempData= oldBackGroundBalanceTransferUserDAO.save(data);
oldBackrUserAttachmentDAO.deleteByEventId(tempData.getId());
if(tempData!=null) {
String[] pics = tempData.getAttachPics().split(",");
String[] fileNames = tempData.getAttachFileNames().split(",");
String[] fileTypes = tempData.getAttachFileTypes().split(",");
//保存附件
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(pics[0])) {
for (int i = 0; i < pics.length; i++) {
OldBackGroundBalanceTransferUserAttachment attachment = new OldBackGroundBalanceTransferUserAttachment();
attachment.setFileUrl(pics[i]);
attachment.setFileName(fileNames[i]);
attachment.setFileType(Integer.valueOf(fileTypes[i]));
attachment.setEventId(tempData.getId());
attachment.setCdate(new Date());
oldBackGroundBalanceTransferUserAttachmentDAO.save(attachment);
}
}
}
}
4、文件压缩下载
@ApiOperation(
value = "zip文件下载",
notes = "zip文件下载",
consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE,
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE,
response = String.class)
@GetMapping(value = "zipDownload", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public void zipDownload(HttpServletResponse response, String fileDir) throws IOException {
log.info("文件管理--------zip文件下载--------请求参数{}", fileDir);
File dirFile = new File(fileDir);
if (!dirFile.exists()) {
throw new BusinessException("文件不存在");
}
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition",
"attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(dirFile.getName() + ".zip", "UTF-8"));
List<Pair<String, InputStream>> filePairs = getFilePairs(dirFile);
ZipOutputStream zipOut = new ZipOutputStream(response.getOutputStream());
for (Pair<String, InputStream> pair : filePairs) {
ZipEntry zipEntry = new ZipEntry(pair.getLeft());
zipOut.putNextEntry(zipEntry);
InputStream inputStream = pair.getRight();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
zipOut.write(bytes, 0, length);
}
inputStream.close();
}
zipOut.close();
}
private List<Pair<String, InputStream>> getFilePairs(File dirFile) throws FileNotFoundException {
List<Pair<String, InputStream>> pairList = new ArrayList<>();
File[] files = dirFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
Pair<String, InputStream> pair = Pair.of(file.getName(), new FileInputStream(file));
pairList.add(pair);
}
return pairList;
}
@ApiOperation(
value = "zip文件下载2",
notes = "zip文件下载2",
consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE,
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE,
response = String.class)
@GetMapping(value = "zipDownload2", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public void zipDownload2(HttpServletResponse response, String fileDir) {
log.info("文件管理--------zip文件下载2--------请求参数{}", fileDir);
File dirFile = new File(fileDir);
if (!dirFile.exists()) {
throw new BusinessException("文件不存在");
}
//2、压缩
ZipUtils.compress(fileDir);
//3、压缩文件下载
File file = new File(fileDir + ".zip");
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition",
"attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(file.getName() + ".zip", "UTF-8"));
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, response.getOutputStream());
response.flushBuffer();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("文件下载异常", e);
throw new RuntimeException("文件下载异常");
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("inputStream流关闭失败", e);
}
}
}
}
四、工具操作
1、Inputstream -> 本地文件
copyInputStreamToFile(InputStream source, File destination)
File localFile = new File(tempFile,fileName);
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(file.getInputStream(),localFile);
2、源文件 -> 本地文件
1)MultipartFile 文件 -> 本地文件
transferTo(File var1)
File localFile = new File(tempFile,fileName);
file.transferTo(localFile);
2)File 文件 ->本地文件
FileUtils.copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile)
3、MultipartFile 文件获取字节 -> OutputStream
byte[] bytes = file.getBytes();
File localFile = new File(tempFile,fileName);
BufferedOutputStream stream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(localFile));
stream.write(bytes);
4、InputStream -> OutputStream
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
5、文件 Url ->InputStream
URL url = new URL(StringEscapeUtils.unescapeHtml(netUrl));
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
conn.setConnectTimeout(30*1000);
conn.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.0; Windows NT; DigExt)");
InputStream stream = conn.getInputStream();
6、图片Url -> OutStream
URL urlStr = new URL(url);
BufferedImage bufferedImage = ImageIO.read(urlStr);
ImageIO.write(bufferedImage, "jpg", response.getOutputStream());
7、Inputstream –>String
IOUtils.toString(super.getInputStream(), "utf-8");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D://test1.txt");
List<String> lines = IOUtils.readLines(is);
8、Inputstream –> byte[]
IOUtils.toByteArray(inputStream)
9、String –> Inputstream
InputStream is = IOUtils.toInputStream("hello world");
10、String –> Outputstream
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:/test.txt");
IOUtils.write("hello write!",os);
五、流关闭
1、流为什么一定要关闭
首先需要明白的一点是GC是回收内存的,关于文件。网络Io,它是属于系统资源的 ,GC只管内存不管别的资源,GC只能回收内存。假如有内存以外的其它资源依附在Java对象上,比如文件,比如输入输出设备(键盘/屏幕等),等等。这些是不能自动关闭,需要我们手动关闭
流不单在内存中分配了空间,也在操作系统占有了资源,java的gc是能从内存中回收不使用的对象,但对操作系统分配的资源是无能为力的,所以就要调用close()方法来通知OS来释放这个资源,然后才可以GC回收。
close()方法是关闭,而GC是销毁。
其实这很象垃圾桶和垃圾工厂的关系,我们把垃圾放入垃圾桶,垃圾并没有被销毁,只是表明:这东西我不要(close())了。而垃圾工厂才是真的把垃圾给处理了。如果你不把垃圾放入垃圾桶(没有close()),垃圾工厂是不敢冲到你家,把垃圾拿去销毁的。
一般情况下是:先打开的后关闭,后打开的先关闭
-
包装关系:可以只关闭处理流(包装流),不用关闭节点流。处理流关闭的时候,会调用其处理的节点流的关闭方法。
-
依赖关系,如果流a依赖流b,应该先关闭流a,再关闭流b。例如,处理流a依赖节点流b,应该先关闭处理流a,再关闭节点流b
节点流:可以从或向一个特定的地方(节点)读写数据。如FileReader.
处理流(包装流):是对一个已存在的流的连接和封装,通过所封装的流的功能调用实现数据读写。如BufferedReader.处理流的构造方法总是要带一个其他的流对象做参数。一个流对象经过其他流的多次包装,称为流的链接。
2、流的正确关闭姿势
1)try catch,要在finaly 中关闭流
/**
* 1.1、try catch,要在finaly 中关闭流
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
File file = new File("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
//TODO 操作代码
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("fileOutputStream未正确关闭");
}
}
}
}
2)应该在循环中关闭流,不应该在循环外
/**
* 1.2、应该在循环中关闭流,如下
*/
@Test
public void closeStream2() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt");
//TODO 操作代码
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("fileOutputStream未正确关闭");
}
}
}
}
}
3)java7 解锁关闭流新姿势
引入了, OutputStream implements Closeable ,所以直接在try里面写上对于的流就可以关闭
/**
* 1.3、java7解决关闭流新姿势
* 只要实现的自动关闭接口(Closeable)的类都可以在try结构体上定义,java会自动帮我们关闭,及时在发生异常的情况下也会。可以在try结构体上定义多个,用分号隔开即可,如:
*/
@Test
public void java6CloseStream() {
try (FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt"); FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt");) {
//TODO 操作代码
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
3、关闭处理流(包装流)
可以只关闭处理流(包装流),包装流的
close方法是会自动关闭被包装的流
1)测试代码
@Test
public void baozhuang(){
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt");
bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
bufferedOutputStream.write("test write something".getBytes());
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
}catch (Exception e){
if(bufferedOutputStream !=null){
//从包装流中关闭流
try {
bufferedOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
log.error("fileOutputStream未正确关闭",ex);
}
}
}
log.info("已经正确关闭了流");
}
2)测试代码拆解
观察
new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream);,BufferedOutputStream继承自FilterOutputStream(一定要看清不是FileOutputStream),它并没有重写close方法,而是直接使用的FilterOutputStream里面的close方法,一定要看清在try里面使用了关闭流的新姿势
class FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream {
@SuppressWarnings("try")
public void close() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream ostream = out) {
flush();
}
}
BufferedOutputStream的构造器直接将FileOutputStream作为属性传入了,通过上面的源码可以知道是在flush()结束之后关闭的是FileOutputStream 文件流
public class BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream { ...
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this(out, 8192);
}
观察FileOutputStream的close方法,可以看出它采用同步锁,而且使用了关闭标记,如果已经关闭了则不会再次操作,所以多次调用不会出现问题。也就是重复调用close()方法不会出问题
class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream{
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (closed) {
return;
}
closed = true;
}
if (channel != null) {
channel.close();
}
fd.closeAll(new Closeable() {
public void close() throws IOException {
close0();
}
});
}
3)结论
包装的流都会自动调用被包装的流的关闭方法,无需自己调用,也就是说包装流并不是什么流,归根结底,最底层的文件流才是正儿八经的流,通过上面的源码也可以看出,有关包装流重复调用包装流和文件流close()方法不会出问题。
4、依赖关系关闭是是有顺序的
1)测试代码
直接调用会抛异常
/**
* 2、流的关闭顺序
* 2.2、依赖关系
*/
@Test
public void baozhuang2() throws Exception {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null;
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt");
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "UTF-8");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
bufferedWriter.write("java IO close test");
// 从内带外顺序顺序会报异常
fileOutputStream.close();
outputStreamWriter();
bufferedWriter.close();//会抛异常
log.info("已经正确关闭了流");
}
java.io.IOException: Stream Closed
at java.io.FileOutputStream.writeBytes(Native Method)
at java.io.FileOutputStream.write(FileOutputStream.java:326)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamEncoder.writeBytes(StreamEncoder.java:221)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamEncoder.implClose(StreamEncoder.java:316)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamEncoder.close(StreamEncoder.java:149)
at java.io.OutputStreamWriter.close(OutputStreamWriter.java:233)
at java.io.BufferedWriter.close(BufferedWriter.java:266)
at com.healerjean.proj.a_test.d03_流关闭.baozhuang2(d03_流关闭.java:128)
2)拆解分析
观察BufferedWriter的关闭源码,可以看到它是直接调用的out也就是文件流 FileOutputStream 流,而我们先关闭了FileOutputStream 流,所以肯定会抛出异常,流已经关闭
public class BufferedWriter extends Writer
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (out == null) {
return;
}
try (Writer w = out) {
flushBuffer();
} finally {
out = null;
cb = null;
}
}
}
void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (nextChar == 0)
return;
out.write(cb, 0, nextChar);
nextChar = 0;
}
}
}
正确写法
/**
* 2、流的关闭顺序
* 1、依赖关系
*/
@Test
public void baozhuang2() throws Exception {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null;
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/test/file.txt");
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "UTF-8");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
bufferedWriter.write("java IO close test");
// // 从内带外顺序顺序会报异常
// fileOutputStream.close();
// outputStreamWriter.close();
// bufferedWriter.close(); //会抛异常
// 正确关闭姿势
bufferedWriter.close();
outputStreamWriter.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
log.info("已经正确关闭了流");
}
3)结论
依赖关系:如果流a依赖流b,应该先关闭流a,再关闭流b。例如,处理流a依赖节点流b,应该先关闭处理流a,再关闭节点流b
5、Flush 是干什么的
Stream也提供了close()方法关闭输出流,以便释放系统资源。要特别注意:OutputStream还提供了一个flush()方法,它的目的是将缓冲区的内容真正输出到目的地。
1)为什么要有flush
因为向磁盘、网络写入数据的时候,出于效率的考虑,操作系统并不是输出一个字节就立刻写入到文件或者发送到网络,而是把输出的字节先放到内存的一个缓冲区里(本质上就是一个
byte[]数组) ,等到缓冲区写满了,再一次性写入文件或者网络,·OutputStream有个flush()方法,能强制把缓冲区内容输出。
2)一定要调用吗
通常情况下,我们不需要调用这个
flush()方法,因为缓冲区写满了OutputStream会自动调用它,并且,在调用close()方法关闭OutputStream之前,也会自动调用flush()方法。
但是,在某些情况下,我们必须手动调用flush()方法
小明正在开发一款在线聊天软件,当用户输入一句话后,就通过
OutputStream的write()方法写入网络流。小明测试的时候发现,发送方输入后,接收方根本收不到任何信息?原因就在于写入网络流是先写入内存缓冲区,等缓冲区满了才会一次性发送到网络。如果缓冲区大小是4K,则发送方要敲几千个字符后,操作系统才会把缓冲区的内容发送出去,这个时候,接收方会一次性收到大量消息。
3)close 和 flush (结论)
flush()方法
1.用来刷新缓冲区,刷新后可以再次写出,这个典型的应用可以脑补下QQ即时聊天场景就好
close()方法
2.用来关闭流释放资源
3.如果是带缓冲区的流对象的close()方法,不但会关闭流,还会在关闭流之前刷新缓冲区,关闭之后不能再写入
所以,不能用close来代替flush
一般情况下,我们也可以使用 close 来进行刷新,通过看 close 方法的源码,发现 close 方法里面包含一个 flush方法。flush 就是刷新缓冲区的功能,所以,我们可以总结 close 方法的作用或者特点是:
1、具备刷新功能,在关闭流之前,就会先刷新一次缓存区,将缓冲区的字节全都刷新到文件上,再关闭流。
2、没有 close 方法,也就是没有进行刷新操作,文件有可能会变小。文件变小,说明了还有一部分内容没有完成写入到文件。前面一篇,我们介绍了缓冲区默认大小是8192字节,上面文件在最后一次写入到文件的缓冲区里,里面字节数没有8192大小,所以不会触发自动写入操作,从而留下一部分字节没有写入到文件。只要文件不是8192字节的N倍大小,如果最后不进行close操作,肯定会丢失一部分数据。
3、一般建议加上 flush
4)fulsh 的使用
InputStream input = httpconn.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = input.read(buffer)) > -1 ) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
baos.flush();
InputStream stream1 = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
//TODO:显示到前台
InputStream stream2 = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
//TODO:本地缓存
六、工具类
1、SFTP
package com.healerjean.proj.util.file;
import com.jcraft.jsch.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Vector;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SFTPUtil {
private static final String encoding = "UTF-8";
@Value("${sftp.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${sftp.port}")
private String portStr;
@Value("${sftp.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${sftp.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${sftp.remotePath}")
private String remotePath;
@Value("${sftp.rsa}")
private String rsa;
/**
* 使用配置文件连接
*/
private ChannelSftp connect() {
ChannelSftp sftp = null;
try {
JSch jsch = new JSch();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(rsa)) {
jsch.addIdentity(rsa);
}
int port = Integer.valueOf(portStr);
Session sshSession = jsch.getSession(username, host, port);
log.info("Session created");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(rsa)) {
sshSession.setPassword(password);
}
Properties sshConfig = new Properties();
sshConfig.put("StrictHostKeyChecking", "no");
sshSession.setConfig(sshConfig);
sshSession.connect();
log.info("Session connected");
log.info("Opening Channel");
Channel channel = sshSession.openChannel("sftp");
channel.connect();
sftp = (ChannelSftp) channel;
log.info("Connected to {}", host);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("Connected to {} failed", host, e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
return sftp;
}
/**
* 手动连接SFTP
*/
private ChannelSftp handConnect(String rsa, String host, String portStr, String username, String password) {
ChannelSftp sftp = null;
try {
JSch jsch = new JSch();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(rsa)) {
jsch.addIdentity(rsa);
}
int port = Integer.valueOf(portStr);
Session sshSession = jsch.getSession(username, host, port);
log.info("Session created");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(rsa)) {
sshSession.setPassword(password);
}
Properties sshConfig = new Properties();
sshConfig.put("StrictHostKeyChecking", "no");
sshSession.setConfig(sshConfig);
sshSession.connect();
log.info("Session connected");
log.info("Opening Channel");
Channel channel = sshSession.openChannel("sftp");
channel.connect();
sftp = (ChannelSftp) channel;
log.info("Connected to {}", host);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("Connected to {} failed", host, e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
return sftp;
}
/**
* 断开连接
*/
private void disconnect(ChannelSftp sftp) {
if (sftp != null) {
if (sftp.isConnected()) {
sftp.disconnect();
log.info("sftp is disconnecting");
} else if (sftp.isClosed()) {
log.info("sftp is already closed");
}
try {
if (sftp.getSession().isConnected()) {
sftp.getSession().disconnect();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("sftp session is disconnect", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
/**
* 去读Sfto文件
*
* @param directory 目录
* @param remoteFileName 远程文件名
* @return
*/
public String readSFTPFile(String directory, String remoteFileName) {
ChannelSftp sftp = connect();
return readSFTPFile(remotePath + directory, remoteFileName, sftp);
}
/**
* @param remoteDirectory 远程目录 比如 /asset/test
* @param remoteFileName 远程文件名
* @param sftp
* @return
*/
private String readSFTPFile(String remoteDirectory, String remoteFileName, ChannelSftp sftp) {
if (sftp == null) {
log.error("connect to sftp failed");
return "false";
}
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader reader = null;
InputStream ins = null;
try {
sftp.cd(remoteDirectory);
ins = sftp.get(remoteFileName);
if (ins == null) {
log.error("filename is not exit");
return "";
}
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ins, encoding));
String inLine = reader.readLine();
while (inLine != null) {
builder.append(inLine);
builder.append("\n");
inLine = reader.readLine();
}
} catch (SftpException se) {
log.info("read sftp {} error ", remoteFileName, se);
throw new RuntimeException(se.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("read sftp {} error ", remoteFileName, e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
if (ins != null) {
ins.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("read ftpFile close InputStream or BufferedReader error ", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
disconnect(sftp);
}
return builder.toString();
}
/**
* 下载单个文件到本地文件
*
* @param directory 远程目录
* @param remoteFileName 远程文件名
* @param downLoadLocalPath 本地下载后存储路径
* @param localFileName 本地下载后的文件名
* @return
*/
public boolean downloadFile(String directory, String remoteFileName, String downLoadLocalPath, String localFileName) {
ChannelSftp sftp = this.connect();
return downloadFile(remotePath + directory, remoteFileName, downLoadLocalPath, localFileName, sftp);
}
/**
* 下载单个文件到本地文件
*
* @param remoteDirectory 远程目录 比如 /asset/test
* @param remoteFileName 远程文件名
* @param downLoadLocalPath 本地下载后存储路径
* @param localFileName 本地下载后的文件名
* @return
*/
private boolean downloadFile(String remoteDirectory, String remoteFileName, String downLoadLocalPath, String localFileName, ChannelSftp sftp) {
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
File file = new File(downLoadLocalPath, localFileName);
File parentFile = file.getParentFile();
if (!parentFile.exists()) {
parentFile.mkdirs();
}
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
out = new FileOutputStream(file);
sftp.get(remoteDirectory + "/" + remoteFileName, out);
log.info("down load single file success , {}", remoteFileName);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("get file error", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
} finally {
if (out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("download single file close error", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}
this.disconnect(sftp);
}
}
/**
* 批量下载文件
*
* @param remoteDirectory 远程下载的目录
* @param downLoadLocalPath 下载的本地路径
* @param fileStartFormat 文件名开头格式
* @param del
* @return
*/
public boolean batchDownLoadFile(String remoteDirectory, String fileStartFormat, String downLoadLocalPath, boolean del, ChannelSftp sftp) {
try {
File directory = new File(downLoadLocalPath);
if (!directory.exists()) {
directory.mkdirs();
}
Vector v = listFiles(remoteDirectory, sftp);
if (v.size() > 0) {
log.info("batch down files start");
Iterator iterator = v.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
ChannelSftp.LsEntry lsEntry = (ChannelSftp.LsEntry) iterator.next();
final String filename = lsEntry.getFilename();
SftpATTRS attrs = lsEntry.getAttrs();
//不是目录
if (!attrs.isDir()) {
//文件格式
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(fileStartFormat)) {
if (filename.startsWith(fileStartFormat)) {
if (downloadFile(remoteDirectory, filename, downLoadLocalPath, filename, sftp) && del) {
deleteSFTPFile(remoteDirectory, filename, sftp);
}
}
} else {
if (downloadFile(remoteDirectory, filename, downLoadLocalPath, filename, sftp) && del) {
deleteSFTPFile(remoteDirectory, filename, sftp);
}
}
}
}//while end
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("batch down files error", e);
return false;
} finally {
this.disconnect(sftp);
}
return true;
}
/**
* 批量下载文件
*
* @param directory 目录
* @param downLoadLocalPath 下载的本地路径
* @param fileStartFormat 文件名开头格式
* @param del
* @return
*/
public boolean batchDownLoadFile(String directory, String fileStartFormat, String downLoadLocalPath, boolean del) {
ChannelSftp sftp = this.connect();
return batchDownLoadFile(remotePath, fileStartFormat, downLoadLocalPath, del, sftp);
}
/**
* @param remoteDirectory 远程上传目录
* @param uploadFileName 上传的文件名
* @param inputStream 上传的流
* @param sftp
* @return
*/
public boolean uploadFile(String remoteDirectory, String uploadFileName, InputStream inputStream, ChannelSftp sftp) {
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 1; i < 3; i++) {
log.info("开始第" + i + "次上传文件,名称 {}", uploadFileName);
try {
createDirAndCd(remoteDirectory, sftp);
sftp.put(inputStream, uploadFileName);
flag = true;
log.info("第" + i + "次上传文件成功,名称 {}", uploadFileName);
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("occurs exception", e);
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("occurs exception", e);
}
}
this.disconnect(sftp);
}
if (i == 3 && !flag) {
log.info("上传3次均失败,文件名称 {}", uploadFileName);
}
}
return flag;
}
/**
* @param directory 目录
* @param remoteFileName 上传的文件名
* @param inputStream
* @return
*/
public boolean uploadFile(String directory, String remoteFileName, InputStream inputStream) {
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
log.info("开始第" + i + "次上传文件,名称 {}", remoteFileName);
ChannelSftp sftp = this.connect();
FileInputStream in = null;
try {
createDirAndCd(remotePath + "/" + directory, sftp);
sftp.put(inputStream, remoteFileName);
flag = true;
log.info("第" + i + "次上传文件成功,名称 {}", remoteFileName);
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("occurs exception", e);
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("occurs exception", e);
}
}
this.disconnect(sftp);
}
if (i == 3 && !flag) {
log.info("上传3次均失败,商户 {},文件名称 {}", remoteFileName);
// AlarmMailLog.logTask("上传3次均失败,商户 " + merchantId + ",文件 "+localFileName);
}
}//for 循环结束
return flag;
}
/**
* 创建目录 并切换到创建的目录下面
*/
private boolean createDirAndCd(String createpath, ChannelSftp sftp) {
try {
if (isDirExist(createpath, sftp)) {
sftp.cd(createpath);
return true;
}
String pathArry[] = createpath.split("/");
StringBuffer filePath = new StringBuffer("");
for (String path : pathArry) {
if (path.equals("")) {
continue;
}
filePath.append(path + "/");
if (isDirExist(filePath.toString(), sftp)) {
sftp.cd(filePath.toString());
filePath.delete(0, filePath.length());
} else {
// 建立目录
sftp.mkdir(filePath.toString());
// 进入并设置为当前目录
sftp.cd(filePath.toString());
filePath.delete(0, filePath.length());
}
}
return true;
} catch (SftpException e) {
log.error("occurs exception", e);
}
return false;
}
private Vector listFiles(String remoteDirectory, ChannelSftp sftp) throws SftpException {
return sftp.ls(remoteDirectory);
}
public Vector listFiles(String directory) {
ChannelSftp sftp = this.connect();
try {
return listFiles(remotePath + directory, sftp);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("列举远程目录下文件出错", e);
return null;
} finally {
this.disconnect(sftp);
}
}
private void deleteSFTPFile(String directory, String deleteFile, ChannelSftp sftp) {
try {
sftp.cd(directory);
sftp.rm(deleteFile);
log.info("delete remote file success {}", deleteFile);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("delete remote file fail", e);
}
}
/**
* 判断目录是否存在
*/
private boolean isDirExist(String directory, ChannelSftp sftp) {
boolean isDirExistFlag = false;
try {
SftpATTRS sftpATTRS = sftp.lstat(directory);
isDirExistFlag = true;
return sftpATTRS.isDir();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (e.getMessage().toLowerCase().equals("no such file")) {
isDirExistFlag = false;
}
}
return isDirExistFlag;
}
/**
* 测试
* 1、连接Sftp
* 2、读取sftp文件内容
* 3、下载sftp文件
* 4、上传文件
* 5、批量下载文件
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SFTPUtil sftpUtil = new SFTPUtil();
//1、连接Sftp
ChannelSftp sftp = sftpUtil.handConnect("D:/work/sftp/id_rsa", "127.0.0.1", "22", "asset", null);
//2、读取sftp文件内容
//远程目录
// String remoteDirectory = "/asset/test";
//文件名
// String remoteFileName = "check_info_result.txt";
// String content = sftpUtil.readSFTPFile(remoteDirectory,remoteFileName,sftp);
// System.out.println(content);
// 3、下载sftp文件
// String downLoadLocalPath = "D:/work/sftp/temp";
// String downLoadFileName = "NEW.TXT" ;
// sftpUtil.downloadFile(remoteDirectory,remoteFileName,downLoadLocalPath,downLoadFileName,sftp);
// 4、上传文件
// String uploadFileName = "upload_NEW.TXT";
// try {
// FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/work/sftp/temp/NEW.TXT");
// sftpUtil.uploadFile(remoteDirectory,uploadFileName,inputStream,sftp);
// } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//5、批量下载文件
// String downLoadLocalPath = "D:/work/sftp/temp";
// sftpUtil.batchDownLoadFile(remoteDirectory,"u",downLoadLocalPath,false,sftp);
//断开连接
sftpUtil.disconnect(sftp);
}
}
2、FTP
package com.healerjean.proj.util.file;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClient;
import org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPReply;
import java.io.*;
@Slf4j
public class FtpUtil {
private FTPClient ftpClient;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FtpUtil t = new FtpUtil();
t.connect("E:\resourse", "10.3.250.74", 21, "HealerJean", "147094");
File file = new File("D:/test");
t.upload(file);
}
/**
* @param path 上传到ftp服务器哪个路径下
* @param addr 地址
* @param port 端口号
* @param username 用户名
* @param password 密码
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private boolean connect(String path, String addr, int port, String username, String password) throws Exception {
boolean result = false;
ftpClient = new FTPClient();
int reply;
//连接ftp 默认是21 不写port也可以
ftpClient.connect(addr, port);
ftpClient.connect(addr);
//ftp登录
ftpClient.login(username, password);
//文件类型为二进制文件
ftpClient.setFileType(FTPClient.BINARY_FILE_TYPE);
reply = ftpClient.getReplyCode();
//保存到ftp路径下
if (!FTPReply.isPositiveCompletion(reply)) {
ftpClient.disconnect();
return result;
}
ftpClient.changeWorkingDirectory(path);
result = true;
return result;
}
/**
* 关闭FTP连接
*/
private void closeConnect() {
if (ftpClient != null && ftpClient.isConnected()) {
try {
ftpClient.logout();
ftpClient.disconnect();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("关闭FTP连接失败", e);
}
}
}
/**
* 上传
*/
private void upload(File file) throws Exception {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
ftpClient.makeDirectory(file.getName());
ftpClient.changeWorkingDirectory(file.getName());
String[] files = file.list();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
File file1 = new File(file.getPath() + "\\" + files[i]);
if (file1.isDirectory()) {
upload(file1);
//上传目录
ftpClient.changeToParentDirectory();
} else {
File file2 = new File(file.getPath() + "\\" + files[i]);
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(file2);
//上传文件
ftpClient.storeFile(file2.getName(), input);
input.close();
}
}
} else {
File file2 = new File(file.getPath());
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(file2);
//上传文件
ftpClient.storeFile(file2.getName(), input);
input.close();
}
}
/**
* 下载该目录下所有文件到本地
* @param ftpPath FTP服务器上的相对路径,例如:test/123
* @param savePath 保存文件到本地的路径,例如:D:/test
*/
public void downloadFiles(String ftpPath, String savePath) {
// 登录
if (ftpClient != null) {
try {
// 判断是否存在该目录
if (!ftpClient.changeWorkingDirectory(ftpPath)) {
throw new RuntimeException("ftp目录不存在");
}
// 设置被动模式,开通一个端口来传输数据
ftpClient.enterLocalPassiveMode();
String[] listNames = ftpClient.listNames();
// 判断该目录下是否有文件
if (listNames == null || listNames.length == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("ftp目录下文件不存在");
}
for (String fileNmae : listNames) {
File file = new File(savePath + '/' + fileNmae);
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
ftpClient.retrieveFile(fileNmae, os);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("文件下载出错", e);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("文件下载出错", e);
}
}
}
}
3、文件 ContentType枚举
package com.hlj.util.Z017_文件ContentType;
/**
* @author HealerJean
* @ClassName FileEnum
* @date 2019/11/7 19:58.
* @Description
*/
public interface FileEnum {
/**
* 文件类型枚举
*/
enum FileContentTypeEnum {
doc(".doc","application/msword"),
docx(".docx","application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document"),
xls(".xls","application/vnd.ms-excel"),
xlsx(".xlsx","application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet"),
csv(".csv","text/csv"),
ppt(".ppt","application/vnd.ms-powerpoint"),
ttf(".ttf","font/ttf"),
js(".js","text/javascript"),
css(".css","text/css"),
xml(".xml","text/xml"),
html(".html","text/html"),
htm(".htm","text/html"),
json(".json","application/json"),
xhtml(".xhtml","application/xhtml+xml"),
jpeg(".jpeg","image/jpeg"),
jpg(".jpg","image/jpeg"),
png(".png","image/png"),
gif(".gif","image/gif"),
ico(".ico","image/vnd.microsoft.icon"),
tif(".tif","image/tiff"),
tiff(".tiff","image/tiff"),
jar(".jar","application/java-archive"),
zip(".zip","application/zip"),
tar(".tar","application/x-tar"),
sh(".sh","application/x-sh"),
mp3(".mp3","audio/mpeg"),
;
private String code;
private String mime;
FileContentTypeEnum(String code, String mime) {
this.code = code;
this.mime = mime;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMime() {
return mime;
}
public void setMime(String mime) {
this.mime = mime;
}
public static FileContentTypeEnum toEnum(String code) {
for (FileContentTypeEnum item : FileContentTypeEnum.values()) {
if (item.getCode().equals(code)) {
return item;
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
4、目录压缩
package com.fintech.scf.utils.zip;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.tools.ant.Project;
import org.apache.tools.ant.taskdefs.Zip;
import org.apache.tools.ant.types.FileSet;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author HealerJean
* @ClassName ZipUtils
* @Date 2019/11/14 20:48.
* @Description 压缩工具类
* <!--zip压缩-->
* <dependency>
* <groupId>org.apache.ant</groupId>
* <artifactId>ant-apache-xalan2</artifactId>
* <version>1.10.1</version>
* </dependency>
*/
@Slf4j
public class ZipUtils {
/**
* 压缩目录
*/
public static void compress(String directoryPath) {
compress(directoryPath, directoryPath+".zip");
}
/**
* 压缩目录
* @param directoryPath 源目录
* @param zipFilePath 目标压缩文件
*/
public static void compress(String directoryPath, String zipFilePath) {
File directory = new File(directoryPath);
if (!directory.exists()) {
log.info("需要被压缩的路径:{}不存在", directoryPath);
throw new RuntimeException(directoryPath + "不存在!");
}
Project prj = new Project();
Zip zip = new Zip();
zip.setProject(prj);
File zipFile = new File(zipFilePath);
zip.setDestFile(zipFile);
FileSet fileSet = new FileSet();
fileSet.setProject(prj);
fileSet.setDir(directory);
//fileSet.setIncludes("**/*.java"); //包括哪些文件或文件夹 eg:zip.setIncludes("*.java");
//fileSet.setExcludes(...); //排除哪些文件或文件夹
zip.addFileset(fileSet);
zip.execute();
}
}
问题
1、不使用递归遍历整个目录
问题:给定一个根目录,要求遍历其中的文件及子文件夹,返回所有后缀是.txt的文件List,不能使用递归
* 作者 :HealerJean
* 日期 :2019/3/13 下午2:34.
* 类描述:给定一个根目录,要求遍历其中的文件及子文件夹,返回所有后缀是.txt的文件List
* * 要求:
* * 1. 不能使用递归
*/
public class Solution {
@Test
public void test() {
File root = new File("/Users/healerjean/Desktop/faceFile");
System.out.println(findTxt(root).toString());
}
/**
* @param root 为一个文件夹根目录
*/
public List<File> findTxt(File root) {
List<File> listTxtFiles = new ArrayList<>();
if (root.exists()) {
//创建一个目录集合,用于存放跟目录下面的文件夹
LinkedList<File> directorys = new LinkedList<>();
//获取根目录下面的子目录文件夹(如果本目录下面包含txt文件,则直接加入listTxtFiles集合中)
File[] files = root.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
//判断是否为目录,然后
if (file.isDirectory()) {
directorys.add(file);
} else if (file.getName().endsWith(".txt")) {
listTxtFiles.add(new File(file.getAbsolutePath()));
}
}
//创建一个临时目录,用于遍历directorys 集合中一个文件夹,如果是我们需要的txt文件,则直接加入集合中,如果该目录下包含子目录,则继续添加到directorys 集合中
File temp_file;
while (!directorys.isEmpty()) {
//每次遍历directorys 中的第一个目录,遍历之前将它作废
temp_file = directorys.removeFirst();
files = temp_file.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
directorys.add(file);
} else if (file.getName().endsWith(".txt")) {
listTxtFiles.add(new File(file.getAbsolutePath()));
}
}
}
}
return listTxtFiles;
}
}
2、文件路径问题
参考博客:关于获取资源文件,Class.getResource和ClassLoader.getResource的区别
1)Jar 路径
String ttcp = this.class.getClassLoader().getResource(ttc).getPath();
if (StringUtils.indexOf(ttcp, "jar!/") > 0) {
ttcp = "jar:" + ttcp;
}
2)Class.getResource 和 ClassLoader.getResource
classpath:WEB-INF/classes下的文件
getResource("")获取的是当前类所在包的路径,而getResource("/")获取的是classpath根路径;
hlj-file
┌─src
│ └─main
│ └─java
│ └─com.healerjean.proj
│ ├─test
│ │ └─GetResourceTest.java
│ └─SpringbootApplication.java
└─resource
├─mapper
│ └─BlogDao.xml
└─confog.properties
a、Class.getResource
1、当以
"/"开头时,是从classpath路径开始匹配资源;2、当不以
"/"开头时,是从当前类所在包的路径开始匹配资源3、两种方式都可以通过
"/"或"../"在文件夹上下层路径切换;
@Test
public void classGetResource() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getResource(""));
// file:/E:/workspace/hlj-file/target/classes/com/healerjean/proj/test/
System.out.println(this.getClass().getResource("/"));
// file:/E:/workspace/hlj-file/target/classes/
// null
System.out.println(this.getClass().getResource("BlogDao.xml"));
System.out.println(this.getClass().getResource("/config.properties"));
// file:/E:/workspace/hlj-file/target/classes/config.properties
System.out.println(this.getClass().getResource("/mapper/BlogDao.xml"));
// file:/E:/workspace/hlj-file/target/classes/mapper/BlogDao.xml
}
b、ClassLoader.getResource()
ClassLoader().getResource获取路径时,不能以"/"开头,且路径总是从classpath根路径开始;
@Test
public void classLoaderGetResource() {
// file:/E:/workspace/hlj-file/target/classes/
System.out.println(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(""));
// null
System.out.println(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/"));
}
3)webroot目录
String srcPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/NamePath.properties");
4)ClassPath其他方法
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("cert/wechat/apiclient_cert.p12");
// 获取文件
File file = resource.getFile();
InputStream certinputStream = resource.getInputStream();
ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:template");
Resource[] resources = ArrayUtils.addAll(
applicationContext.getResources("classpath*:com/admore/dao/mybatis/**/mysql/*.xml"),
applicationContext.getResources("classpath*:com/admore
3、InputStream 对象的重复使用 以及 fush 正确写法
InputStream input = httpconn.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = input.read(buffer)) > -1 ) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
baos.flush();
InputStream stream1 = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
//TODO:显示到前台
InputStream stream2 = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
//TODO:本地缓存