SQL大全之_函数
前言
Github:https://github.com/HealerJean
1、日期相关
1.1、(时间/日期)之差
1.1.1、timestampdiff :
时间之差
-- 后面减去前面的
select timestampdiff(day, '2020-01-02', '2020-01-01') as diff ; -- -1
select timestampdiff(day, '2020-01-01', '2020-01-02') as diff ; -- 1
| 单位 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SECOND | 秒 |
| MINUTE | 分钟 |
| HOUR | 小时 |
| DAY | 天 |
| MONTH | 月 |
| YEAR | 年 |
1.1.2、datediff
天数之差
select datediff('2020-01-02','2020-01-01') as diff ; -- 1
1.2、(时间/日期)加/减数字-> 日期
1.2.1、date_add
date_add(date,INTERVAL expr type)
select date_add('2020-01-02' ,interval 1 day) as dateofafter; -- 2020-01-03
select date_add('2020-01-02' ,interval 1 month ) as dateofafter; -- 2020-02-02
select date_add('2020-01-02' ,interval 1 second ) as dateofafter; -- 2020-01-02 00:00:01
1.2.2、date_sub
date_sub(date,INTERVAL expr type)
select date_sub('2020-01-02' ,interval 1 day) as dateofafter; -- 2020-01-01
select date_sub('2020-01-02' ,interval 1 month ) as dateofafter; -- 2019-12-02
select date_sub('2020-01-02' ,interval 1 second ) as dateofafter; -- 2020-01-01 23:59:59
1.3、字符串和(时间/日期)互转
create table date_test(
id bigint(20) not null auto_increment ,
name varchar(20) default '',
yyyyMMdd date default null ,
yyyyMMddHHmmss datetime default null ,
primary key (id)
)
INSERT INTO date_test (id, name, yyyyMMdd, yyyyMMddHHmmss) VALUES (1, 'healerjean', '2018-12-12', '2018-12-12 23:11:11');
1.3.1、date_format
日期转字符串
-- yyyyMMddHHmmss 存储数据为 2018-12-12 23:11:11
select * from date_test d where date_format(d.yyyyMMddHHmmss,"%Y-%m-%d") = '2018-12-12';
select * from date_test d where date_format(d.yyyyMMddHHmmss,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s") = '2018-12-12 23:11:11';
-- yyyyMMdd 存储的为 2018-12-12
select * from date_test d where date_format(d.yyyyMMdd,"%Y-%m-%d") = '2018-12-12';
-- 下面这个找不到数据,说明date类型默认的时分秒 为00:00:00
select * from date_test d where date_format(d.yyyyMMdd, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s") = '2018-12-12 00:00:00';
1.3.2、str_to_date
字符串转日期
-- 注意哦,下面这种我们匹配数据库中一定存在的,不可以类似于format那样模糊查询,因为条件是我们字数输入的
select * from date_test d where d.yyyyMMdd = STR_TO_DATE('2018-12-12','%Y-%m-%d') ;
select * from date_test d where d.yyyyMMdd = STR_TO_DATE('2018-12-12 00:00:00','%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s') ;
select str_to_date('08/09/2008', '%m/%d/%Y'); -- 2008-08-09
select str_to_date('08/09/08' , '%m/%d/%y'); -- 2008-08-09
select str_to_date('08.09.2008', '%m.%d.%Y'); -- 2008-08-09
select str_to_date('08:09:30', '%h:%i:%s'); -- 08:09:30
select str_to_date('08.09.2008 08:09:30', '%m.%d.%Y %h:%i:%s'); -- 2008-08-09 08:09:30
1.4、时间戳和时间互转
MICROSECOND
SECOND
MINUTE
HOUR
DAY
WEEK
MONTH
QUARTER
YEAR
SECOND_MICROSECOND
MINUTE_MICROSECOND
MINUTE_SECOND
HOUR_MICROSECOND
HOUR_SECOND
HOUR_MINUTE
DAY_MICROSECOND
DAY_SECOND
DAY_MINUTE
DAY_HOUR
YEAR_MONTH
1.4.1、unix_timestamp:
获取日期的时间戳,毫秒
select unix_timestamp(); -- 1218290027
select unix_timestamp('2008-08-08'); -- 1218124800
select unix_timestamp('2008-08-08 12:30:00'); -- 1218169800
2.16.4、from_unixtime
时间戳转化为日期(时间戳为毫秒)
select from_unixtime(1218290027); -- '2008-08-09 21:53:47'
select from_unixtime(1218169800, '%Y %D %M %h:%i:%s %x'); -- '2008 8th August 12:30:00 2008'
1.5、天数和日期互转
1.5.1、 to_days(date), :
select to_days('0000-00-00'); -- 0
select to_days('2008-08-08'); -- 733627
1.5.2、from_days(days)
select from_days(738010); -- 2020-08-08
1.6、秒和时间互转
1.6.1、time_to_sec(time)
select time_to_sec('01:00:05'); -- 3605
1.6.2、 sec_to_time(seconds)
select sec_to_time(3605); -- '01:00:05'
1.7、拼凑时间/日期
1.7.1、makdedate(year,dayofyear)
select makedate(2001,31); -- '2001-01-31'
select makedate(2001,32); -- '2001-02-01'
1.7.2、maketime(hour,minute,second)
(拼凑日期、时间函数:)
select maketime(12,15,30); -- '12:15:30'
1.8、查询一些特定日期
今天
select * from 表名 where to_days(时间字段名) = to_days(now());
昨天
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE TO_DAYS( NOW( ) ) - TO_DAYS( 时间字段名) <= 1
7天
SELECT * FROM 表名 where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 7 DAY) <= date(时间字段名)
近30天
SELECT * FROM 表名 where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 30 DAY) <= date(时间字段名)
本月
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE DATE_FORMAT( 时间字段名, '%Y%m' ) = DATE_FORMAT( CURDATE( ) , '%Y%m' )
上一月
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE PERIOD_DIFF( date_format( now( ) , '%Y%m' ) , date_format( 时间字段名, '%Y%m' ) ) =1
#查询本季度数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where quarter(create_date)=quarter(now());
#查询上季度数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where QUARTER(create_date)=QUARTER(DATE_SUB(now(),interval 1 QUARTER));
#查询本年数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where YEAR(create_date)=YEAR(NOW());
#查询上年数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where year(create_date)=year(date_sub(now(),interval 1 year));
查询当前这周的数据
SELECT name,submittime FROM enterprise WHERE YEARWEEK(date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m-%d'))
= YEARWEEK(now());
查询上周的数据
SELECT name,submittime FROM enterprise WHERE YEARWEEK(date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m-%d')) = YEARWEEK(now())-1;
查询当前月份的数据
select name,submittime from enterprise where date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m')=date_format(now(),'%Y-%m')
查询距离当前现在6个月的数据
select name,submittime from enterprise where submittime between date_sub(now(),interval 6 month) and now();
1.9、时间截取
天
select substring('2023-01-01 00::00:00', 1 ,10);
--2023-01-01
月
select substring('2023-01-01 00::00:00', 1 ,7);
年
select substring('2023-01-01 00::00:00', 1 ,4);
开发中心
substr(policy_date, 1, 10)
2、case when (试着和if进行替换使用)
2.1、普通使用
case cp.ssid when 'aa' then '0' else'1' end as flag
2.2、复杂条件
以下场景 我们要扣减金额 operateMoney ,并且要求分配额度和临时额度扣减完成必须大于 0 字段说明:
分配额度 allot_amount
临时额度 temp_amount
总额度 total_amount
总额度直接减去total_amount
判断临时额度是否 大于等于 扣减的额度,
如果大于,那么直接扣减临时额度,分配额度不变
如果小于,则是先扣减临时额度,然后再扣减分配额度
使用主键进行更新,只锁一行,当id和 当分配额度和临时额度扣减后是否大于0 成立的时候更新
update scf_risk_department_limit set
total_amount = total_amount - #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL},
available_amount = available_amount - #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL},
allot_amount = (
case when temp_amount >= #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL}
then allot_amount
else allot_amount - ( #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL} - temp_amount )
end ),
temp_amount = (
case when temp_amount >= #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL}
then temp_amount - #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL}
else 0
end )
where id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
and (allot_amount + temp_amount ) > #{operateMoney,jdbcType=DECIMAL}
2.3、case 中 when和and一起使用
update driver_online
set vRemainCapacity = case when (vRemainCapacity>0) and ((vRemainCapacity-0.5) >0)
then vRemainCapacity-0.5
else 0 end
where driverId = 'DR120161118100001';
2.4、case 、when 多个条件
update goods
set price = (
case
when price between 0 and 99 then price * 1.2
when price between 100 and 999 then price * 1.1
when price between 1000 and 1999 then price * 1.05
when price > 1999
then price * 1.02
end);
select * from goods;
2.5、case的目标 中添加函数
select substr(t1.area_id, 1, 1) type,
substr(t1.area_id, 2) id,
case substr(t1.area_id, 1, 1)
when 'c' then
(select t2.country
from countnumber.dbtable_countryid t2
where t2.id = substr(t1.area_id, 2))
else
(select distinct t3.province
from countnumber.dbtable_provinceid t3
where t3.id = substr(t1.area_id, 2))
end name
from t_ad_area t1
2.6、where中使用case
求男生的平均分大于女的班级
SELECT class
FROM TestResults
GROUP BY class
HAVING AVG(CASE WHEN sex = '男'
THEN score
ELSE NULL END)
< AVG(CASE WHEN sex = '女'
THEN score
ELSE NULL END)
求出不同班级中男生和女生的数量
select class,
sum(case when sex="男" then 1 else 0 end) as numOfMan,
sum(case when sex="女" then 1 else 0 end) as numOfWoman
from gg group by class;
3、If 函数使用
select if( 1 > 0 ,1 ,0 ) ;
IF(expr1,expr2,expr3)
expr1 是TRUE 返回 expr2 否则返回 expr3
4、运算
4.1、加减乘除
| 运算 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|
| 加 | + | |
| 减 | - | |
| 乘 | * | |
| 除 | /、div | select 1/0 from dual ; 余数可以为0,得到的结果为NUll |
| 余数 | %、mod |
4.2、power:n次幂
power(x,y) --返回 x 的 y 次方
select power(2,3) ; -- 8
4.3、sqrt:平方根
select sqrt(4); -- 2
4.4、rand()
rand()函数返回的是一个小于1的随机数**
select rand();
4.4.1、使用案例1:随机查询
1、一般情况,rand() 性能比较差
select c.url from coupon_item_good 5 order by rand() limit 1
2、优化,round() 进行优化
随机选择一个id,然后选择一个大于他的数据,limit控制为1
随机选择一个推广位,具体条件就是下面and中连接的and t1.status 开始
select *
from `coupon_adzone` as t1
join (select round(rand() * (select max(id)
from `coupon_adzone`)
) as id) as t2
where t1.id >= t2.id
and t1.status = 1
and t1.adzonetype = 3
and
order by t1.id asc
limit 1;
4.5、取小数convert round cast
4.5.1、round:推荐使用
round第二个表示小数保留几位,不足的补上0。
第二个如果为负数
-1 代表个位数为0 ROUND(114.6,-1) 结果 110,
-2 代表个位数和十分位 为0 ROUND(114.6,-2) 结果 100
ROUND(100.3465,2) 100.35
ROUND(100,2), 100
ROUND(0.6,2), 0.60
ROUND(114.6,-1) 110
4.5.2、convert
select convert(10000,decimal(10,2));
# 四舍五入,decimal(10,2)后面的代表最大长度10以及保留的小数位数2
select convert(10569.3645,decimal(10,2)); #10569.36
select convert(10569.3665555,decimal(10,2)); #10569.37
4.5.3、cast:强制转换
select cast(10*1/4 as decimal(18,2)) from dual
4.6、abs:函数取绝对值
有时候项目中出现两个数字相减,可能是负数,但是只是需要这连个数的差值,所以就需要用它
ABS( TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE,i.cdate,#{createTime}) ))< #{adzoneTime})
4.7、floor:向下取整
SELECT FLOOR(25.75); -- 25
2.13、拼接字符串
2.13.1、concat:普通拼接
如果有一个参数为null,则返回结果为null
SELECT CONCAT(’My’, NULL, ‘QL’);
NULL
模糊查询使用concat('%',#{params},'%'))
<if test="params != null and params != ''">
u.nickName like concat('%',#{params},'%')
</if>
2.13.2、concat_ws,分隔符连接字符串
第一个参数是其它参数的分隔符。分隔符的位置放在要连接的两个字符串之间。分隔符可以是一个字符串,也可以是其它参数。
如果分隔符为 NULL,则结果为 NULL ,函数会忽略任何分隔符参数后的 NULL 值。
SELECT CONCAT_WS(',','First name','Second name','Last Name');
First name,Second name,Last Name
SELECT CONCAT_WS(',','First name','','Last Name');
First name,,Last Name (空字符串不会忽略)
SELECT CONCAT_WS(',','First name',null ,'Last Name');
First name,Last Name
2.14、locate: 出现的index位置
SELECT LOCATE('bar', 'foobarbar'); #4
SELECT LOCATE('xbar', 'foobarbar'); #0
位置从4开始数起
SELECT LOCATE('bar', 'foobarbar',4); # 4
项目使用
查找具有http字段的用户
select * from users where locate('http',itemUrl);
判断site表中的url是否包含'http://'子串,如果不包含则拼接在url字符串开头
update site set url =concat('http://',url) where locate('http://',url)=0;
5、ifnull
如果为空返回第二个,如果不空返回第一个
ifnull(b.realName,c.realName) authName,
6、isnull、length
函数:判断是否为null或空字符串
isnull(aBegBalRule) || length (trim(aBegBalRule))<1
7、group_concat
语句将某一列的值查询成逗号分隔的字符串
select group_concat(c.id) from coupon_item_good;
返回结果
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33
8、find_in_set
查询字段为逗号隔开的字段属性
字段 pnum为逗号隔开的字符串
1,2,3,4,21,9
select * from test t where find_in_set(2,t.pnum) ;
9、like 匹配
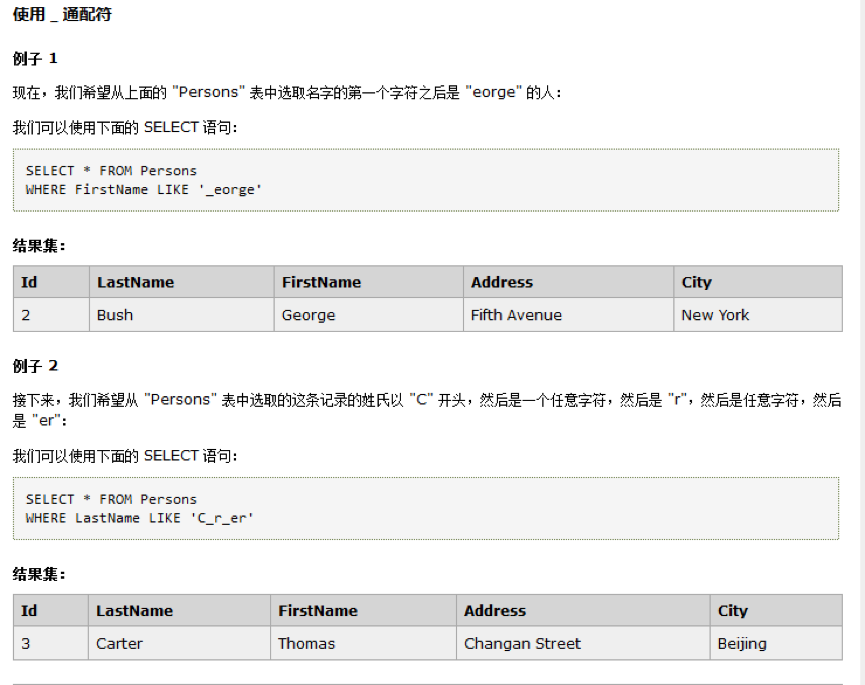
9.1、_
表示任意单个字符。匹配单个任意字符
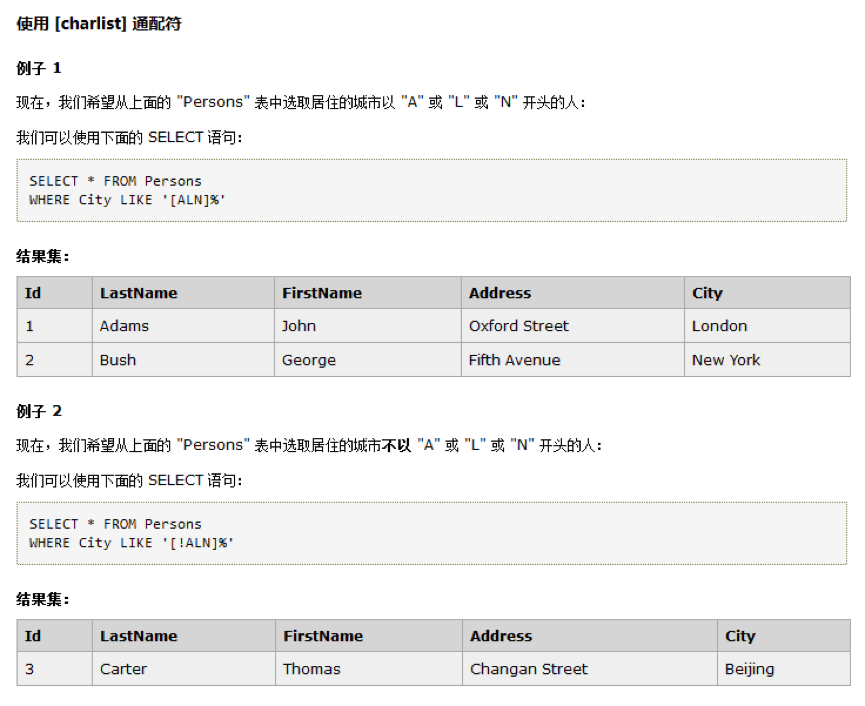
9.2、[charlist]
只要在里面存在就匹配
10、any、in、some、all
any,all关键字必须与一个比较操作符一起使用
10.1、any/some
any关键词可以理解为“对于子查询返回的列中的任一数值,如果比较结果为true,则返回tuue
some是any的别名,用法相同。
select s1 from t1 where s1 > any (select s1 from t2);
-- 选择count(*) 在中间的,不包含最大和最小的
select activity as ACTIVITY,
count(*)
from friends
group by activity
having count(*) > any ( select count(*) from friends group by activity)
and count(*) < any ( select count(*) from friends group by activity);
10.2、all
all的意思是“对于子查询返回的列中的所有值,如果比较结果为true,则返回true”
select s1 from t1 where s1 > all(select s1 from t2);
11、on duplicate key update
若表
A数据在插入时有冲突,则直接自动转为根据唯一索引进行更新的操作。如果在insert语句末尾指定了on duplicate key update1、如果在一个
unique索引或primary key中出现重复值,则在出现重复值的行执行update;2、如果不会导致唯一值列重复的问题,则插入新行。
<update id="insertOrUpdate" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" parameterType="com.healerjean.proj.data.pojo" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into h_table_name
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="bikeId != null">
bike_id,
</if>
<if test="batteryId != null">
battery_id,
</if>
<if test="retryCount != null">
retry_count,
</if>
<if test="dataSource != null">
data_source,
</if>
<if test="enable != null">
`enable`,
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time,
</if>
<if test="updateTime != null">
update_time,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="bikeId != null">
#{bikeId,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="batteryId != null">
#{batteryId,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="retryCount != null">
#{retryCount,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="dataSource != null">
#{dataSource,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="enable != null">
#{enable,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
#{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="updateTime != null">
#{updateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
</trim>
on duplicate key
<trim prefix="update" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="bikeId != null">
bike_id = #{bikeId,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="batteryId != null">
battery_id = #{batteryId,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="retryCount != null">
retry_count = #{retryCount,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="dataSource != null">
data_source = #{dataSource,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="enable != null">
`enable` = #{enable,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time = #{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="updateTime != null">
update_time = #{updateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
</trim>
</update>
11.1、insert 1行记录
案例1:
1、例如,如果列 a 为 主键 或 拥有UNIQUE索引,并且包含值1,则以下两个语句具有相同的效果:
insert into table (a,c) values (1,3) on duplicate key update c = c + 1;
update table set c = c + 1 where a = 1;
11.2、insert 多行记录
2、如果INSERT多行记录(假设 a 为主键或 a 是一个 UNIQUE索引列):
insert into table (a,c) values (1,3),(1,7) on duplicate key update c = c + 1;
11.3、Id自增问题解决
有一个很坑的地方,那就是本次操作并没有进行插入,而是一个更新操作,主键
id会进行自增。由于这个原因,这种也一般只在数据量很大,
id对业务影响不大,批量插入/更新的时候使用
11.3.1、方案1、修改内核参数
有一种方式是通过修改
MySQL内核参数innodb_autoinc_lock_mode来解决。这个参数控制着在向有auto_increment列的表插入数据时,相关锁的行为。
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode 有三个取值:0 (tradition)、1(consecutive)、2(interleaved)
1(consecutive):数据库默认,就会发生上面的那种现象。每次使用insert into … on duplicate key update 的时候,数据库只是简单地自增id,不管实际是insert还是update操作。
0 (tradition)将该参数改为 0 后,数据库则只有在实际发生insert的时候才会自增主键,但是每次都会锁表,并发性不太好。考虑到性能问题,没有使用这种方案。
11.3.2、方案2:不处理,业务放不使用id作为关联字段
其实若是修改表结构,在表
B中存入表A中的业务字段(唯一键信息),而不是A的主键,也能解决这个问题。 但是若频繁使用on duplicate key update,表A中自增主键id依然会跳跃增加,造成不必要的浪费。
11.4、总结
1、ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE 需要有在 INSERT 语句中有存在主键或者唯一索引的列,并且对应的数据已经在表中才会执行更新操作。若表有多个唯一索引,则酌情使用(默认选择第一个,按索引被添加到表上的顺序排序)
2、更新的字段是主键或者唯一索引,不能和表中已有的数据重复,否则插入更新都失败。
3、本次操作并没有进行插入,而是一个更新操作,主键id会进行自增
11.5、问题处理
11.5.1、Too many keys are generated
很明显错误意思是说 数据库生成了多个主键
key而我们需要封装key的参数只有一个,数量上的不对等导致mybatis报错 。⬤
mybatis版本低的时候不会有该问题⬤ 版本高的时候,返回的行数不是插入数据的行数,可能是0,1,2(1代表插入,2代表更新) 比如插入3条数据,其中2条
insert,1条updae,则返回的是5
<insert id="insertOrUpdate" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
去掉
<insert id="insertOrUpdate" >
12、字符串截取
12.1、left ( str, length)
mysql> select left('sqlstudy.com', 3);
+-------------------------+
| left('sqlstudy.com', 3) |
+-------------------------+
| sql |
+-------------------------+
12.1.1、入库自动截取
<insert id="insertSubString">
<![CDATA[
INSERT INTO user (name)
VALUES (left(#{name}, 5) )
]]>
</insert>
12.2、right ( str , length )
mysql> select right('sqlstudy.com', 3);
+--------------------------+
| right('sqlstudy.com', 3) |
+--------------------------+
| com |
+--------------------------+
12.3、substring ( str, pos, len)
1、从字符串的第 4 个字符位置开始取,直到结束。
mysql> select substring('sqlstudy.com', 4);
+------------------------------+
| substring('sqlstudy.com', 4) |
+------------------------------+
| study.com |
+------------------------------+
2、从字符串的第 4 个字符位置开始取,只取 2 个字符。
mysql> select substring('sqlstudy.com', 4, 2);
+---------------------------------+
| substring('sqlstudy.com', 4, 2) |
+---------------------------------+
| st |
+---------------------------------+
3、从字符串的第 4 个字符位置(倒数)开始取,直到结束。
mysql> select substring('sqlstudy.com', -4);
+-------------------------------+
| substring('sqlstudy.com', -4) |
+-------------------------------+
| .com |
+-------------------------------+
4、从字符串的第 4 个字符位置(倒数)开始取,只取 2 个字符。
mysql> select substring('sqlstudy.com', -4, 2);
+----------------------------------+
| substring('sqlstudy.com', -4, 2) |
+----------------------------------+
| .c |
+----------------------------------+
12.4、substring_index ( str, delim , count )
1、截取第二个 ‘.’ 之前的所有字符。
mysql> select substring_index('www.sqlstudy.com.cn', '.', 2);
+------------------------------------------------+
| substring_index('www.sqlstudy.com.cn', '.', 2) |
+------------------------------------------------+
| www.sqlstudy |
+------------------------------------------------+
2、截取第二个 ‘.’ (倒数)之后的所有字符。
mysql> select substring_index('www.sqlstudy.com.cn', '.', -2);
+-------------------------------------------------+
| substring_index('www.sqlstudy.com.cn', '.', -2) |
+-------------------------------------------------+
| com.cn |
+-------------------------------------------------+
3、如果在字符串中找不到 delim 参数指定的值,就返回整个字符串
mysql> select substring_index('www.sqlstudy.com.cn', '.coc', 1);
+---------------------------------------------------+
| substring_index('www.sqlstudy.com.cn', '.coc', 1) |
+---------------------------------------------------+
| www.sqlstudy.com.cn |
+---------------------------------------------------+
13、字符串不足填充
13.1、lpad(str,len,padstr)
返回字符串
str,左填充用字符串padstr填补到len字符长度。⬤ 如果
str为大于len长,返回值被缩短至len个字符(即,不能超过len长)。
select lpad('321',4, '0'); # 0321
select lpad('4321',4,'0'); # 4321
select lpad('54321',4,'0');# 5432
13.2、rpad(str,len,padstr)
返回字符串
str,右填充用字符串padstr填补到len字符长度。⬤ 如果
str为大于len长,返回值被缩短至len个字符(即,不能超过len长)。
select rpad('321',4, '0'); # 3210
select rpad('4321',4,'0'); # 4321
select rpad('54321',4,'0');# 5432